& meet dozens of singles today!
User blogs
CoinDesk reported yesterday that crypto trading startup Coinbase is being valued at $77 billion on private exchanges. And Forbes reported that Stripe is being valued at $115 billion on secondary markets, where private shares can be bought and sold, albeit in a limited fashion.
I instantly wanted to write a piece headlined “Beware those super hot secondary market valuations,“ but after a little digging, I cannot. It turns out that the public markets are so hot, there is historical precedent for seemingly aggressive secondary market transactions being conservative compared to later IPO valuations. And there is further precedent for private market transactions that are more conservative in price terms than venture-determined valuations also working out.
The Exchange explores startups, markets and money. Read it every morning on Extra Crunch, or get The Exchange newsletter every Saturday.
The hot equities market is making stock pickers out of many startup investors, regardless of whether they are leading priced rounds of buying shares on modern secondary markets.
 It’s hard to overvalue a startup when the public market is willing to double its valuation the moment it starts to trade.
It’s hard to overvalue a startup when the public market is willing to double its valuation the moment it starts to trade.
Let’s explore the new prices for Coinbase and Stripe by starting with a look at their dated private valuations, their new, reported secondary prices and where some companies that went public with notable secondary prices wound up trading today.
This will be fun! I promise!
Overprice me, I dare you
Coinbase was last valued by private-market money at around $8 billion, per Crunchbase data back in October of 2018. More recently we’ve seen secondary transactions that value the firm at $50 billion, other notes concerning a $75 billion possible valuation, and even some enthusiastic chat from a former employee that the company could be worth $100 billion.
Its new $77 billion price tag might seem somewhat pedestrian in that mix, but recall that we’re largely discussing the valuations associated with Coinbase set by buyers not in the know; retail secondary buyers of shares in the cryptocurrency exchange are probably not its board members.
So, the public is, to some degree, repricing Coinbase. The question is whether those prices make any sense. Hold your answer, we have more work to do.
Stripe at $115 billion on secondary exchanges is perhaps bonkers, or perhaps nothing more than rationality. In its last round, a $600 million Series G that came in mid-2020, Stripe was valued at around $36 billion. And, it is rumored to be raising capital at a $100 billion valuation.
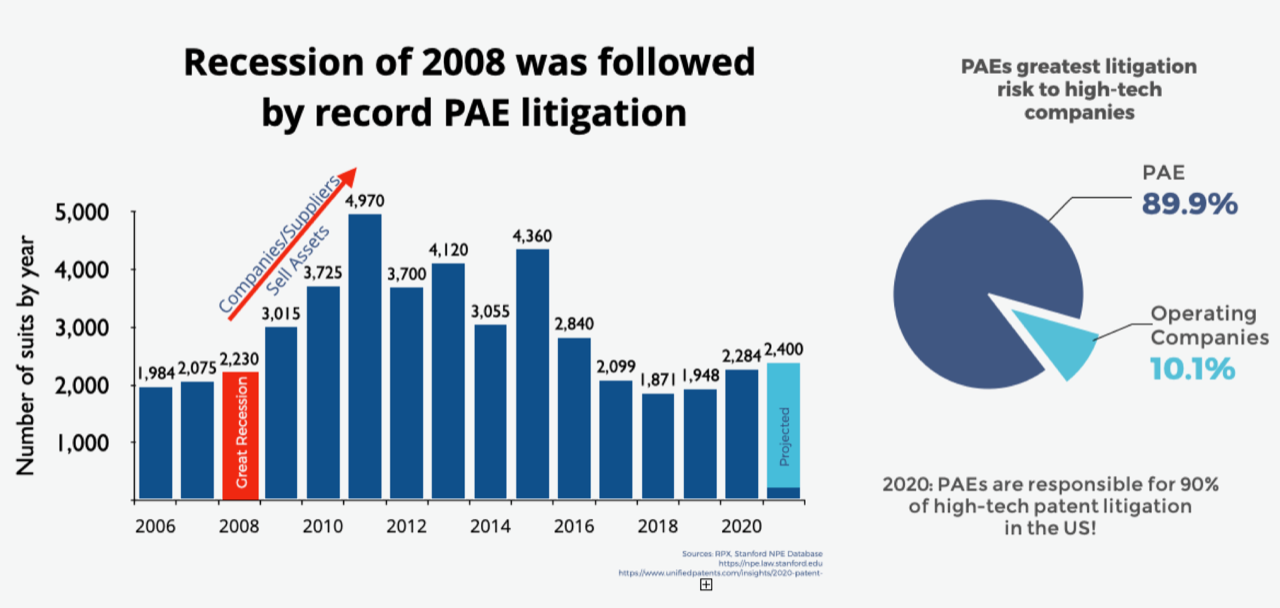
LOT Network, the non-profit that helps businesses of all sizes and across industries defend themselves against patent trolls by creating a shared pool of patents to immunize themselves against them, today announced that TikTik parent ByteDance is joining its group.
ByteDance has acquired its fair share of patents in recent years and is itself embroiled in a patent fight with its rival Triller. That’s not what joining the LOT Network is about, though. ByteDance is joining a group of companies here that includes the likes of IBM, the Coca-Cola Company, Cisco, Lyft, Microsoft, Oracle, Target, Tencent, Tesla, VW, Ford, Waymo, Xiaomi and Zelle. In total, the group now has over 1,300 members.
As LOT CEO Ken Seddon told me, the six-year-old group had a record year in 2020, with 574 companies joining it and bringing its set of immunized patents to over 3 million, including 14% of all patents issued in the U.S.
Among the core features of LOT, which only charges members who make more than $25 million in annual revenue, is that its members aren’t losing control over the patents they add to the pool. They can still buy and trade them as before, but if they decide to sell to what the industry calls a ‘patent assertion entity,’ (PAE) that is, a patent troll, they automatically provide a free licence to that patent to every other member of the group. This essentially turns LOT into what Seddon calls a ‘flu shot ‘ against patent trolls (and one that’s free for startups).
“The conclusion that people are waking up to is, is that we’re basically like a herd, we’re herd immunization, effectively,” Seddon said. “And every time a company joins, people realize that the community of non-members shrinks by one. It’s like those that don’t have the vaccination shrinks — and they are, ‘wait a minute, that makes me a higher risk of getting sued. I’m a bigger target.’ And they’re like, ‘wait a minute, I don’t want to be the target.'”
ByteDance, he argues, is a good example for a company that can profit from membership in LOT. While you may think of patents as purely a sign of a company’s innovativeness, for corporate lawyers, they are also highly effective defense tools (that can be used aggressively as well, if needed). But it can take a small company years to build up a patent portfolio. But a fast-growing, successful company also becomes an obvious target for patent trolls.
“When you are a successful company, you naturally become a target,” Seddon said. “People become jealous and they become threatened by you. And they covet your money and your revenue and your success. One of the ways that companies can defend themselves and protect their innovation is through patents. Some companies grow so fast, they become so successful, that their revenue grows faster than they can grow their patent portfolio organically.” He cited Instacart, which acquired 250 patents from IBM earlier this month, and Airbnb, which was sued by IBM over patent infringement in early 2020 (the companies settled in December), as examples.
ByteDance, thanks to the success of TikTok, now finds itself in a situation where it, too, is likely to become a target of patent trolls. The company has started acquiring patents itself to grow its portfolio faster and now it is joining LOT to strengthen its protection there.
“[ByteDance] is being a visionary and trying to get ahead of the wave,” Seddon noted. “They are a successful global company that needs to develop a global IP strategy. Historically, PAEs were just a US problem, but now ByteDance has to worry about PAEs being an issue in China and Europe as well. By joining LOT, they protect themselves and their investments from over 3 million patents should they ever fall into the hands of a PAE.”
Lynn Wu, Director and Chief IP Counsel, Global IP and Digital Licensing Strategy at ByteDance, agrees. “Innovation is core to the culture at ByteDance, and we believe it’s important to protect our diverse technical and creative community,” she said in today’s announcement. “As champions for the fair use of IP, we encourage other companies to help us make the industry safer by joining LOT Network. If we work together, we can protect the industry from exploitation and continue advancing innovation, which is key to the growth and success of the entire community.”
There’s another reason companies are so eager to join the group now, though, and that’s because these patent assertion entities, which had faded into the background a bit in the mid- to late-2010s, may be making a comeback. The core assumption here is a bit gloomy: many companies seem to assume we’re in for an economic downturn. If we hit a recession, a lot of patent holders will start looking at their patent portfolios and start selling off some their more valuable patents in order to stay afloat. Since beggars can’t be choosers, that often means they’ll sell to a patent troll if that troll is the highest bidder. Last year, a patent troll sued Uber using a patent sold by IBM, for example (and IBM gets a bit of a bad rap for this, but, hey, it’s business).
That’s what happened after the last recession — though it typically takes a few years for the effect to be felt. Nothing in the patent world moves quickly.
Now, when LOT members sell to a troll, that troll can’t sue other LOT members over it. Take IBM, for example, which joined LOT last year.
“People give IBM a lot of grief and criticism for selling to PAEs, but at least IBM is giving everybody a chance to get a free license,” Seddon told me. “IBM joined LOT last year and what IBM is effectively doing is saying to everybody, ‘look, I joined LOT.’ And they put all of their entire patent portfolio into LOT. And they’re saying to everybody, ‘look, I have the right to sell my patents to anybody I want, and I’m going to sell it to the highest bidder. And if I sell it to a patent troll and you don’t join LOT — and if you get sued by a troll, is that my fault or your fault? Because if you join LOT, you could have gotten a free license.'”
A couple of weeks ago SentinelOne announced it was acquiring high-speed logging platform Scalyr for $155 million. Just this morning CrowdStrike struck next, announcing it was buying unlimited logging tool Humio for $400 million.
In Humio, CrowdStrike gets a company that will provide it with the ability to collect unlimited logging information. Most companies have to pick and choose what to log and how long to keep it, but with Humio, they don’t have to make these choices with customers processing multiple terabytes of data every single day.
Humio CEO Geeta Schmidt writing in a company blog post announcing the deal described her company in similar terms to Scalyr, a data lake for log information:
“Humio had become the data lake for these enterprises enabling searches for longer periods of time and from more data sources allowing them to understand their entire environment, prepare for the unknown, proactively prevent issues, recover quickly from incidents, and get to the root cause,” she wrote.
That means with Humio in the fold, CrowdStrike can use this massive amount of data to help deal with threats and attacks in real time as they are happening, rather than reacting to them and trying to figure out what happened later, a point by the way that SentinelOne also made when it purchased Scalyr.
“The combination of real-time analytics and smart filtering built into CrowdStrike’s proprietary Threat Graph and Humio’s blazing-fast log management and index-free data ingestion dramatically accelerates our [eXtended Detection and Response (XDR)] capabilities beyond anything the market has seen to date,” CrowdStrike CEO and co-founder George Kurtz said in a statement.
While two acquisitions don’t necessarily make a trend, it’s clear that security platform players are suddenly seeing the value of being able to process the large amounts of information found in logs, and they are willing to put up some cash to get that capability. It will be interesting to see if any other security companies react with a similar move in the coming months.
Humio was founded in 2016 and raised just over $31 million, according to Pitchbook Data. Its most recent funding round came in March 2020, a $20 million Series B led by Dell Technologies Capital. It would appear to be a decent exit for the startup.
CrowdStrike was founded in 2011 and raised over $480 million along the way before going public in 2019. The deal is expected to close in the first quarter, and is subject to typical regulatory oversight.
California’s Department of Motor Vehicles is warning of a potential data breach after a contractor was hit by ransomware.
The Seattle-based Automatic Funds Transfer Services (AFTS), which the DMV said it has used for verifying changes of address with the national database since 2019, was hit by an unspecified strain of ransomware earlier this month.
In a statement sent by email, the DMV said that the attack may have compromised “the last 20 months of California vehicle registration records that contain names, addresses, license plate numbers and vehicle identification numbers.” But the DMV said AFTS does not have access to customers’ Social Security numbers, dates of birth, voter registration, immigration status or driver’s license information, and was not compromised.
The DMV said it has since stopped all data transfers to AFTS and has since initiated an emergency contract to prevent any downtime.
AFTS is used across the United States to process payments, invoices and verify addresses. Several municipalities have already confirmed that they are affected by the data breach, suggesting it may not be limited to California’s DMV. But it’s not known what kind of ransomware hit AFTS. Ransomware typically encrypts a company’s files and will unlock them in exchange for a ransom. But since many companies have backups, some ransomware groups threaten to publish the stolen files online unless the ransom is paid.
AFTS could not be immediately reached for comment. Its website is offline, with a short message: “The website for AFTS and all related payment processing website [sic] are unavailable due to technical issues. We are working on restoring them as quickly as possible.”
“We are looking at additional measures to implement to bolster security to protect information held by the DMV and companies that we contract with,” said Steve Gordon, the director of the state’s DMV.
Last year it was reported that California’s DMV makes more than $50 million a year by selling drivers’ personal information, including to bondsmen and private investigators.
California has more than 35 million registered vehicles.
Source: https://techcrunch.com/2021/02/18/california-motor-vehicles-afts-ransomware/
The rise of “Zoom University” was only possible because edtech wasn’t ready to address the biggest opportunity of the past year: remote learning at scale. Of course, the term encapsulates more than just Zoom, it’s a nod to how schools had to rapidly adopt enterprise video conferencing software to keep school in session in the wake of closures brought on by the virus’ rapid spread.
Now, nearly a year since students were first sent home because of the coronavirus, a cohort of edtech companies is emerging, emboldened with millions in venture capital, ready to take back the market.
The new wave of startups are slicing and dicing the same market of students and teachers who are fatigued by Zoom University, which — at best — often looks like a gallery view with a chat bar. Four of the companies that are gaining traction include Class, Engageli, Top Hat and InSpace. It signals a shift from startups playing in the supplemental education space and searching to win a spot in the largest chunk of a students day: the classroom.
While each startup has its own unique strategy and product, the founders behind them all need to answer the same question: Can they make digital learning a preferred mode of pedagogy and comprehension — and not merely a backup — after the pandemic is over?
Answering that question begins with deciding whether videoconferencing is what online, live learning should look like.
Ground up
“This is completely grounds up; there is no Zoom, Google Meets or Microsoft Teams anywhere in the vicinity,” said Dan Avida, co-founder of Engageli, just a few minutes into the demo of his product.
Engageli, a new startup founded by Avida, Daphne Koeller and Serge Plotkin, raised $14.5 million in October to bring digital learning to college universities. The startup wants to make big lecture-style classes feel more intimate, and thinks digitizing everything from the professor monologues to side conversations between students is the way to go.
Engageli is a videoconferencing platform in that it connects students and professors over live video, but the real product feature that differentiates it, according to Avida, is in how it views the virtual classroom.
Upon joining the platform, each student is placed at a virtual table with another small group of students. Within those pods, students can chat, trade notes, screenshot the lecture and collaborate, all while hearing a professor lecture simultaneously.

“The FaceTime session going on with friends or any other communication platform is going to happen,” Avida said. “So it might as well run it through our platform.”
The tables can easily be scrambled to promote different conversation or debates, and teachers can pop in and out without leaving their main screen. It’s a riff on Zoom’s breakout rooms, which let participants jump into separate calls within a bigger call.
There’s also a notetaking feature that allows students to screenshot slides and live annotate them within the Engageli platform. Each screenshot comes with a hyperlink that will take the student back to the live recording of that note, which could help with studying.
“We don’t want to be better than Zoom, we want to be different than Zoom,” Avida said. Engageli can run on a variety of products of differing bandwidth, from Chromebooks to iPads and PCs.
Engageli is feature-rich to the point that it has to onboard teachers, its main customer, in two phases, a process that can take over an hour. While Avida says that it only takes five minutes to figure out how to use the platform to hold a class, it does take longer to figure out how to fully take advantage of all the different modules. Teachers and students need to have some sort of digital savviness to be able to use the platform, which is both a barrier to entry for adoption but also a reason why Engageli can tout that it’s better than a simple call. Complexity, as Avida sees it, requires well-worth-it time.
The startup’s ambition doesn’t block it from dealing with contract issues. Other video conferencing platforms can afford to be free or already have been budgeted into. Engageli currently charges $9.99 or less per student seat for its platform. Avida says that with Zoom, “it’s effectively free because people have already paid for it, so we have to demonstrate why we’re much better than those products.”
Engageli’s biggest hurdle is another startup’s biggest advantage.
Built on top of Zoom
Class, launched less than a year ago by Blackboard co-founder Michael Chasen, integrates exclusively with Zoom to offer a more customized classroom for students and teachers alike. The product, currently in private paid beta, helps teachers launch live assignments, track attendance and understand student engagement levels in real time.
While positioning an entire business on Zoom could lead to platform risk, Chasen sees it as a competitive advantage that will help the startup stay relevant after the pandemic.
“We’re not really pitching it as pandemic-related,” Chasen said. “No school has only said that we’re going to plan to use this for a month, and very few K-12 schools say we’re only looking at this in case a pandemic comes again.” Chasen says that most beta customers say online learning will be part of their instructional strategy going forward.
Investors clearly see the opportunity in the company’s strategy, from distribution to execution. Earlier this month, Class announced it had raised $30 million in Series A financing, just 10 weeks after raising a $16 million seed round. Raising that much pre-launch gives the startup key wiggle room, but it also gives validation: a number of Zoom’s earliest investors, including Emergence Capital and Bill Tai, who wrote the first check into Zoom, have put money into Class.
“At Blackboard, we had a six to nine month sales cycle; we’d have to explain that e-learning is a thing,” Chasen said, who was at the LMS business for 15 years. “[With Class] we don’t even have to pitch. It wraps up in a month, and our sales cycle is just showing people the product.
Unlike Engageli, Class is selling to both K-12 institutions and higher-education institutions, which means its product is more focused on access and ease of use instead of specialized features. The startup has over 6,000 institutions, from high schools to higher education institutions, on the waitlist to join.
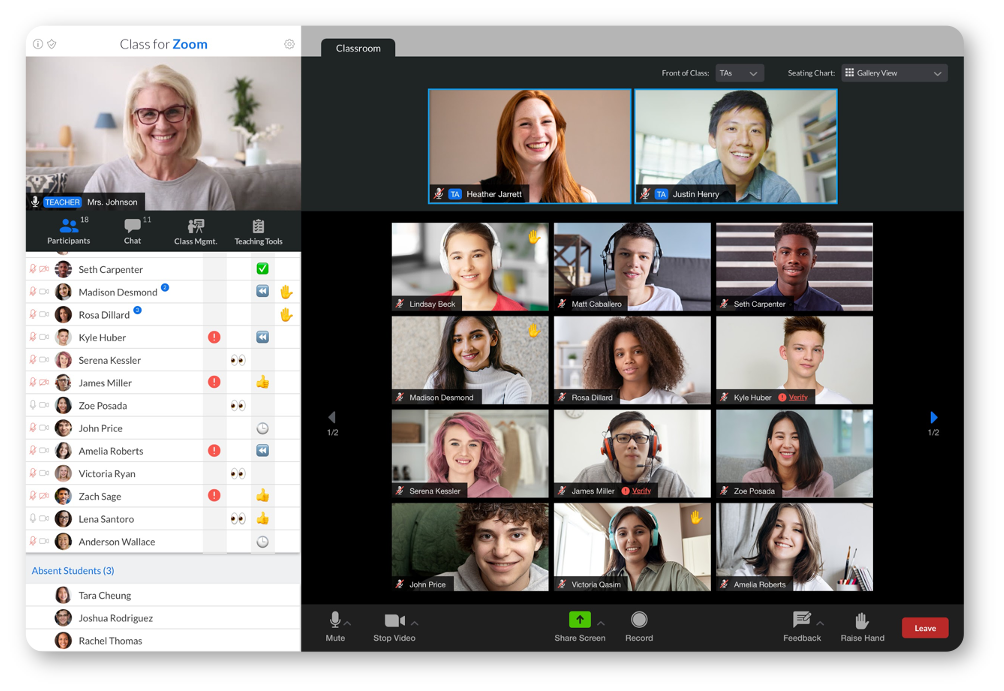
Image Credits: Class
Right now, Class software is only usable on Macs, but its beta will be available on iPhone, Windows and Android in the near future. The public launch is at the end of the quarter.
“K-12 is in a bigger bind,” he said, but higher-ed institutions are fully committed to using synchronous online learning for the “long haul.”
“Higher-ed has already been taking this step towards online learning, and they’re now taking the next step,” he said. “Whereas with a lot of K-12, I’m actually seeing that this is the first step that they’re taking.”
The big hurdle for Class, and any startup selling e-learning solutions to institutions, is post-pandemic utility. While institutions have traditionally been slow to adopt software due to red tape, Chasen says that both of Class’ customers, higher ed and K-12, are actively allocating budget for these tools. The price for Class ranges between $10,000 to $65,000 annually, depending on the number of students in the classes.
“We have not run into a budgeting problem in a single school,” he said. “Higher ed has already been taking this step towards online learning, and they’re now taking the next step, whereas K-12, this is the first step they’re taking.”
Asynchronously, silly
Engageli and Class are both trying to innovate on the live learning experience, but Top Hat, which raised $130 million in a Series E round this past week, thinks that the future is pre-recorded video.
Top Hat digitizes textbooks, but instead of putting a PDF on a screen, the startup fits features such as polls and interactive graphics in the text. The platform has attracted millions of students on this premise.
“We’re seeing a lot of companies putting emphasis on creating a virtual classroom,” he said. “But replicating the same thing in a different medium is never a good idea…nobody wants to stare at a screen and then have the restraint of having to show up at a previous pre-prescribed time.”
In July, Top Hat launched Community to give teachers a way to make class more than just a YouTube video. Similar to ClassDojo, Community provides a space for teachers and students to converse and stay up to date on shared materials. The interface also allows students to create private channels to discuss assignments and work on projects, as well as direct message their teachers.
CEO Mike Silagadze says that Top Hat tried a virtual classroom tool early on, and “very quickly learned that it was fundamentally just the wrong strategy.” His mindset contrasts with the demand that Class and Engageli have proven so far, to which Silagadze says might not be as long-term as they think.
“There’s definitely a lot of interest that’s generated in people signing up to beta lists and like wanting to try it out. But when people really get into it, everyone pretty much drops off and focuses more on asynchronous, small and in-person groups.”
Instead, the founder thinks that “schools are going to double down on the really valuable in-person aspects of higher education that they couldn’t provide before” and deliver other content, like large lecture-style classes or meetings, through asynchronous content delivery.
This is similar to what Jeff Maggioncalda, the CEO of Coursera, told TechCrunch in November: Colleges are going to re-invest in their in-person and residential experiences, and begin offering credentials and content online to fill in the gaps.
“We’ve been on the journey to create a more and more complete platform that our customers can use since almost day one,” Silagadze said. “What the pandemic has brought is much more comprehensive testing functionality that Top Hat has rolled out and better communication tooling so basically better chat and communication tooling for professors.”
Community costs $30 per semester, per student. Currently Top Hat has most of its paying customers coming in through its content offering, the digital textbooks, instead of this learning platform.
College spin-out
InSpace, a startup spinning out of Champlain college, is similarly focused on making the communication between professors and students more natural. Dr. Narine Hall, the founder of the startup, is a professor herself who just wanted class to “feel more natural” when it was being conducted.
InSpace is similar to some of the virtual HQ platforms that have popped up over the past few months. The platforms, which my colleague Devin Coldewey aptly dubbed Sims for Enterprise, are trying to create the feel of an office or classroom online but without a traditional gallery view or conference call vibe. The potential success of inSpace and others could signal how the future of work will blend gaming and socialization for distributed teams.
InSpace is using spatial gaming infrastructure to create spontaneity. The technology allows users to only hear people within their nearby proximity, and get quieter as they walk, or click, away. When applied to a virtual world, spatial technology can give the feeling of a hallway bump-in.
Similar to Engageli, inSpace is rethinking how an actual class is conducted. In inSpace, students don’t have to leave the main call to have a conversation during inSpace, which they do in Zoom. Students can just toggle over to their own areas and a professor can see teamwork being done in real time. When a student has a question, their bubble becomes bigger, which is easier to track than the hand-raise feature, says Hall.
InSpace has a different monetization strategy than other startups. It charges $15 a month per-educator or “host” versus per-student, which Hall says was so educators could close contracts “as fast as possible.” Hall agrees with other founders that schools have a high demand for the product, but she says that the decision-making process around buying new tooling continues to be difficult in schools with tight budgets, even amid a pandemic. There are currently 100 customers on the platform.
So far, Hall sees inSpace working best with classes that include 25 people, with a max of 50 people.
The company was born out of her own frustrations as a teacher. In grad school, Hall worked on research that combined proximity-based interactions with humans. When August rolled around and she needed a better solution than WebEx or Zoom, she turned to that same research and began building code atop of her teachings. It led to inSpace, which recently announced that it has landed $2.5 million in financing led by Boston Seed Capital.
The differences between each startup, from strategy to monetization to its view of the competition, are music to Zoom’s ears. Anne Keough Keehn, who was hired as Zoom’s Global Education Lead just nine months ago, says that the platform has a “very open attitude and policy about looking at how we best integrate…and sometimes that’s going to be a co-opetition.”
“In the past there has been too much consolidation and therefore it limits choices,” Keehn said. “And we know everybody in education likes to have choices.” Zoom will be used differently in a career office versus a class, and in a happy hour versus a wedding; the platform sees opportunity in it all beyond the “monolithic definition” that video-conferencing has had for so long.
And, despite the fact that this type of response is expected by a well-trained executive at a big company in the spotlight, maybe Keehn is onto something here: Maybe the biggest opportunity in edtech right now is that there is opportunity and money in the first place, for remote learning, for better video-conferencing and for more communication.
Source: https://techcrunch.com/2021/02/18/edtech-zoom-university/