& meet dozens of singles today!
User blogs
Volkswagen, once a dabbler in electric vehicles, is now betting its future on the technology. And the new Volkswagen ID.4 — a five-passenger, fully-electric crossover with a starting price of $33,995 (before federal or state incentives) — is its first global effort to make EVs a mainstream product and part of its larger goal to become carbon neutral by 2050.
The upshot: The VW ID.4 offers a balanced blend of technology, comfort and design for a more affordable price and seeks to capture some of the market left vacant by the lack of an affordable Tesla Model Y. The VW ID.4 offers solid technology without being so out-of-this-world that your average crossover buyer will balk with one exception. The lack of seamless charging makes finding and then connecting to a third-party charging station a clunky, even complex experience.
As Mark Gillies, Senior Manager of Product at VW said during our interview, “We want to be the company that builds electric cars for the millions, not just for the millionaires.”
While that may be true, there are a few niggling concerns like a somewhat laggy infotainment system that should improve with updates coming soon, and the previously mentioned miss of seamless charging. If Volkswagen can address those problems, the VW ID.4 could take a solid bite out of the booming crossover market. But will the masses flock to a fully-electric future that delivers a near-to-gasoline driving experience and become the “car for the millions?”
The 2021 Volkswagen ID.4 crossover might be the first global, dedicated all-electric vehicle from the VW brand, but it’s not the first consumer-available electric vehicle from the VW Group as a whole. It launched the California-only Volkswagen e-Golf back in 2013 (discontinued last year), and the company’s luxury performance brand Porsche began sales of its all-electric Taycan in 2019.
When it launched, e-Golf represented more of a fringe case for the company. It was targeted specifically at the California market, where incentives for electric vehicles and charging infrastructure, as well as environmental regulations, are more robust. The ID.4, in contrast, represents one of the “most important Volkswagen debuts since the Beetle,” and it will be available across the country.
The tech that stands out
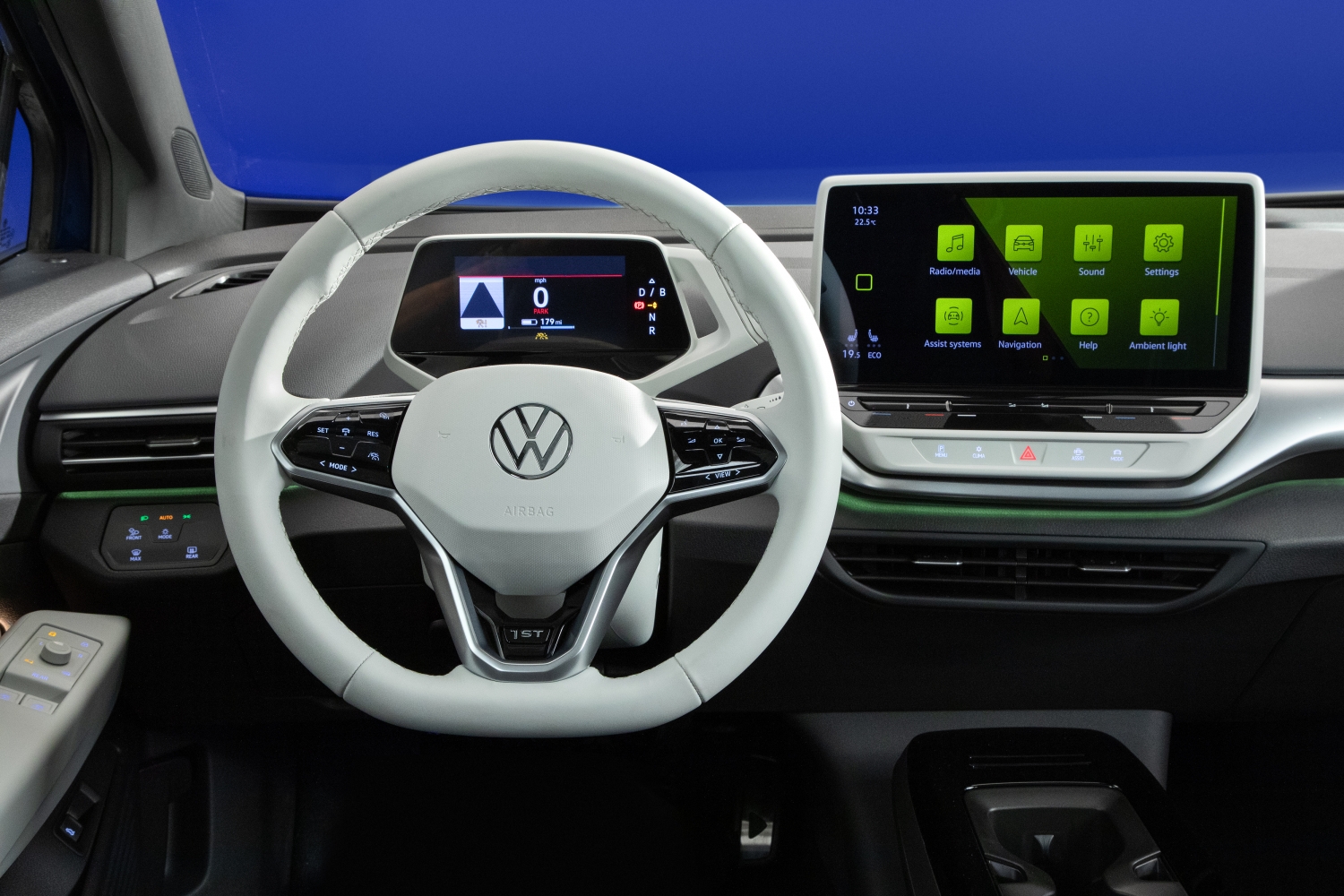
Rather than try to fit a gasoline-shaped peg into an electric-shaped hole, Volkswagen appears to have taken a page from Tesla’s book in its approach to the dash layout and cabin feel in the ID.4.
The interior design of the ID.4 feels like a glimpse of a self-driving future as you could visualize a day when both the steering column and even the infotainment system could simply be deleted. Even the center console, complete with modular cupholders, cubbies and NFC charging pad could eventually be modified to create more passenger space, making the interior of the ID.4. feel even more open and airy than it already does.
The ID.4 launches with three trims: the Pro, Pro S and 1st Edition. The Pro comes with a 10-inch touchscreen. The Pro S and 1st Edition trims come with a 12-inch infotainment touchscreen mounted at the center of the dashboard.
As you reach towards the center screen, the icons respond thanks to an in-cabin camera that tracks hand motion towards the system. There are very few hard-touch buttons inside the ID.4, and those that do exist are more like medical-grade haptic buttons used to control everything from climate and audio to the opening and closing of the shade on the optional panoramic fixed-glass roof and even driving modes and driver assistance features. They take a little getting used to, but once familiar they tend to work like slider buttons, allowing you to adjust volume or temperature with slight pressure changes and small slides from left to right.
Hello I.D.
Instead of buttons, Volkswagen has decided to leverage hands-free voice control in the new ID.4, but during our time with the vehicle, the system felt like it was still in beta.
Both driver and passenger use the touchscreen or specific voice commands to many of the common features and infotainment of the ID.4. Say “Hello I.D.” and a light strip along the base of the windshield lights up based on which side of the vehicle the voice came from (passenger or driver), indicating that it’s ready to receive the command you say next.
Commands are rather limited at this time and must be initiated by either saying the key phrase (“Hello I.D.”) or pushing the voice control button located on the steering wheel. You can say basic things like navigation commands but you can also say things like “I’m cold,” or “tell me a joke,” and the ID.4 system will respond by raising the temperature on that side of the car, or telling a seatbelt joke.
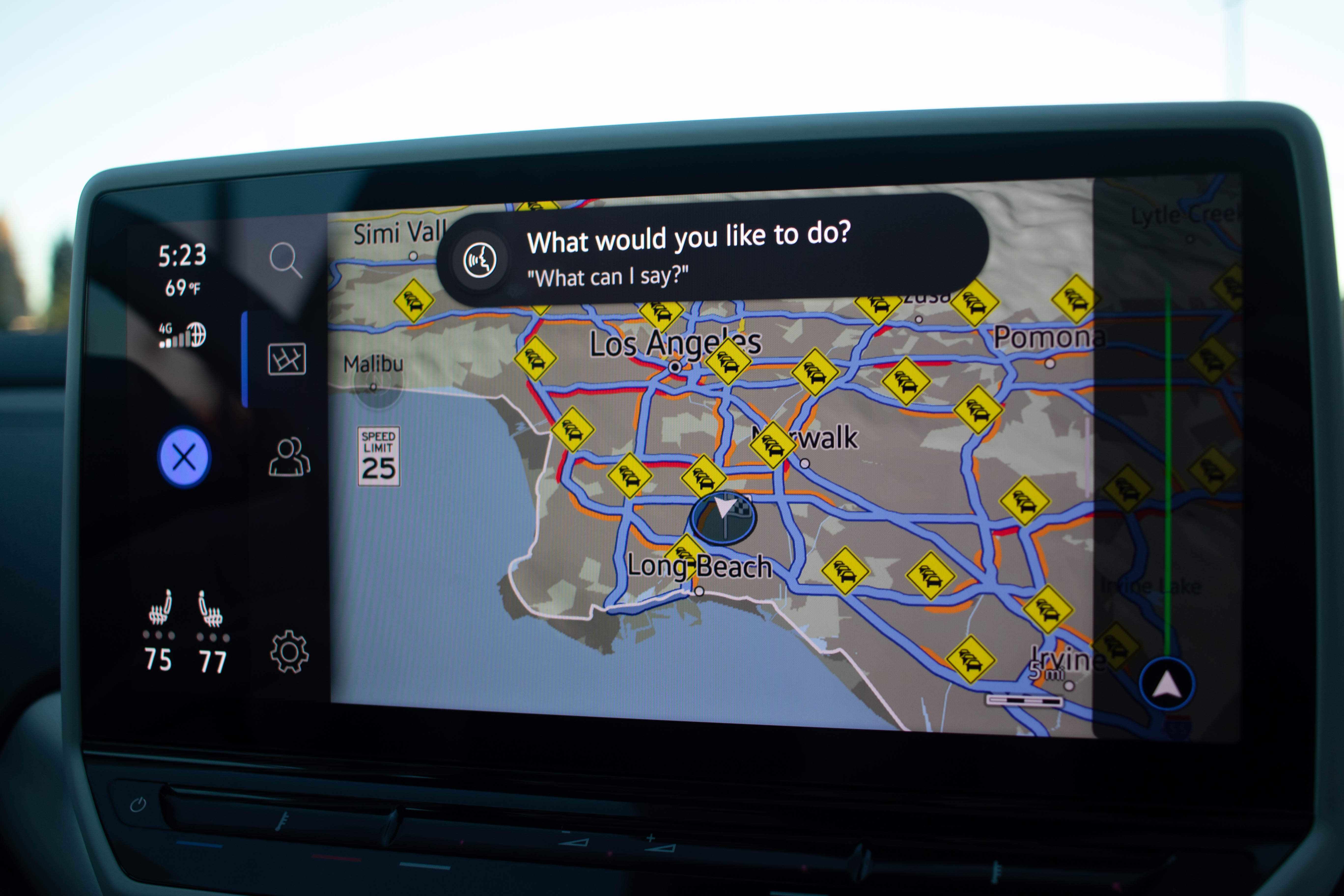
During the test drive, the response time from the system was very slow compared to other voice systems on the market, and it struggled to find connectivity to do things like change a Sirius XM channel, (repeatedly saying that it couldn’t find a specific channel number or name) even though my test drive didn’t stray beyond the bounds of Los Angeles and Long Beach. It also failed more often than naught, taking around ten seconds or more to finally cancel out of the voice control systems when it either couldn’t understand the command or it couldn’t get connectivity.
Laggy nav
The navigation system in the ID.4 was also a bit laggy and imprecise, which meant I reverted to using Google maps and the wireless Android Auto system (included along with Apple CarPlay throughout the ID.4 lineup) to get directions. One neat feature of the ID.4’s on-board navigation system, however, is that the light strip along the windshield illuminates on either side of the vehicle as you approach a turn to indicate which direction you should go.
The infotainment screen looks just like your phone or tablet screen: Swipe through the pages of apps or various windows to get to the page you want. Unfortunately, the combination of a laggy connection to the network (despite having three to five bars of 4G connectivity according to the infotainment system), and a laggy load time, the screens would occasionally freeze while swiping between pages, showing half of one page while still loading the next.
As a caveat: I was lucky enough to get three separate opportunities to spend extended time in different ID.4s in the Los Angeles press fleet and only experienced the lag/freeze with one of the vehicles, however. Volkswagen PR says that the software in the test vehicles is not the final version that customers will receive and it will be updated before getting to owners, which should solve for the strange stuttering and voice command issues that I experienced.
The ID.4 will also get Alexa capability later this year through their Car-Net service which includes an app that can help you monitor your vehicle from afar. The app is simple enough to use: Owners login and can see the location, charge level, and status of their ID.4.
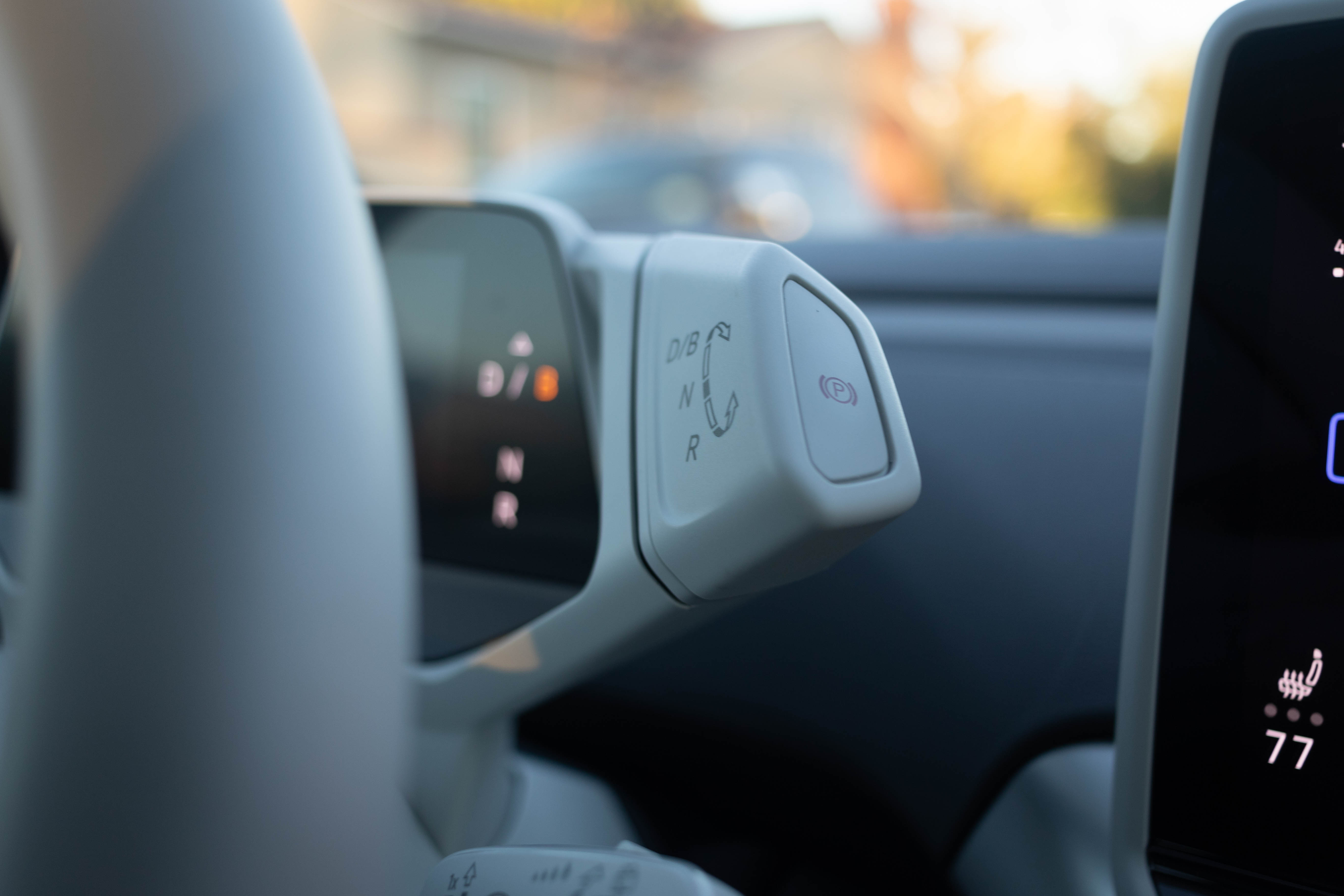
VW made a multitude of interesting design choices inside the ID.4 including the placement of the main instrument panel and the transmission selector. Rather than attaching these items to the dash or center console like you’d find in a typical vehicle, they’re attached directly to the steering column. When you move the steering wheel, the instrument panel and transmission rocker move with it. Volkswagen uses a 5.3-inch screen attached to the steering wheel to provide information about everything from speed and direction of travel to range, trip, and basic navigation information. You use a rhombus-shaped rocker at the right side of the steering wheel to toggle through driving modes rather than a standard button or shift lever.
There’s a start/stop button located in a rather hidden spot on the right side of the column to start the ID.4, but it’s largely superfluous. When you unlock the vehicle and sit in the driver’s seat, the ID.4 powers on and is ready to drive. When you unlatch your seatbelt and climb out, the ID.4 powers down. That makes things a bit complicated if you have friends or family in the vehicle while you dash into a place to run an errand, but the ID.4 allows passengers to keep things like the AC and heat going for a short period of time by using controls that appear on the infotainment screen, even if the driver isn’t in the vehicle.
Converting drivers to EVs
Volkswagen says that its research has shown that roughly 30% of crossover owners would consider an electric crossover. There’s no denying that the ID.4 enters a crowded crossover market complete with extremely popular gasoline and hybrid competitors like the Toyota RAV4 and Honda CR-V. Volkswagen says that, based on its research, consumers shouldn’t feel any range anxiety since most crossover owners drive around 60 miles per day and the battery system offers an EPA-estimated 250 miles of range. You can charge the ID.4 from 5% to 80% in 38 minutes at a 125 kW.
A full charge at home is estimated to take around 7.5 hours but, if you’re out and about, Volkswagen is offering free, unlimited charging at DC fast chargers by Electrify America at no additional cost for the first three years of ID.4 ownership, which sounds great, but comes with some caveats. VW says that it expects most people to charge overnight on typical residential power, and it’s clear that the company doesn’t expect owners to use public chargers all that frequently because the process of locating an available charger is not seamless, at least not at the ID.4’s launch.
Electrify America is a subsidiary of VW, yet they operate completely separately from Volkswagen. The company operates 550 charging stations and more than 2,400 DC fast chargers, across the country. You can search for “charging stations,” through the on-board nav but the system brings up all charging stations in the vicinity and doesn’t show which are online and available and which ones are not. In order to find specific Electrify America chargers, owners have to pull out their phones and open the Electrify America app to see which stations are online and available. You can then send the location of a specific charger to AndroidAuto or Apple CarPlay to navigate. Unfortunately, at this point, the Electrify America app does not show up in Android Auto.
This process is rather clunky and would require owners to pull over and park to safely complete it before heading to the charging station–at least at this point in time. Volkswagen says that an over-the-air update coming later this year will further integrate Electrify America stations into the on-board nav in a more seamless way.
The good news is that the EPA-estimated fuel economy equivalent for the Pro S and 1st Edition models is 104 MPGe for city driving, while highway driving is rated at 89 MPGe, for a combined city/highway rating of 97 MPGe.
One of the striking features of the ID.4 is how it drives. Transmission modes on the ID.4 include a B or brake mode–a common and exceedingly convenient setting that allows for one-pedal driving on electric vehicles. Take your foot off the brake and the ID.4 slows slightly, regenerating electricity and sending it back into the battery. It’s a great feature in stop-and-go traffic and Volkswagen intentionally tuned the one-pedal driving to be less aggressive than those in other electric vehicles, with the aim of making the feel more familiar for first-time electric vehicle owners.
On the road, the ID.4 feels well planted and not nearly as large as it looks. It’s nimble but not exactly quick off the line (VW has not released 0-60 mph times) though it doesn’t leave you sweating to make a short merge. It’s certainly no tire-smoker or rocketship, however.
Since it’s a rather bulbous shape, there is some very minor wind noise at speed on the road, but the ride is comfortable and confident. At speeds below 20 miles an hour (and when you put it into reverse), it does make that characteristic electric car sound to alert pedestrians. It’s not noticeable inside the cabin when the windows are raised, but pass a neighbor who is working on a car in his garage, and you’ll be sure to arrive home to a text asking if that was you driving around in the car that sounds like a spaceship.
ADAS form & function
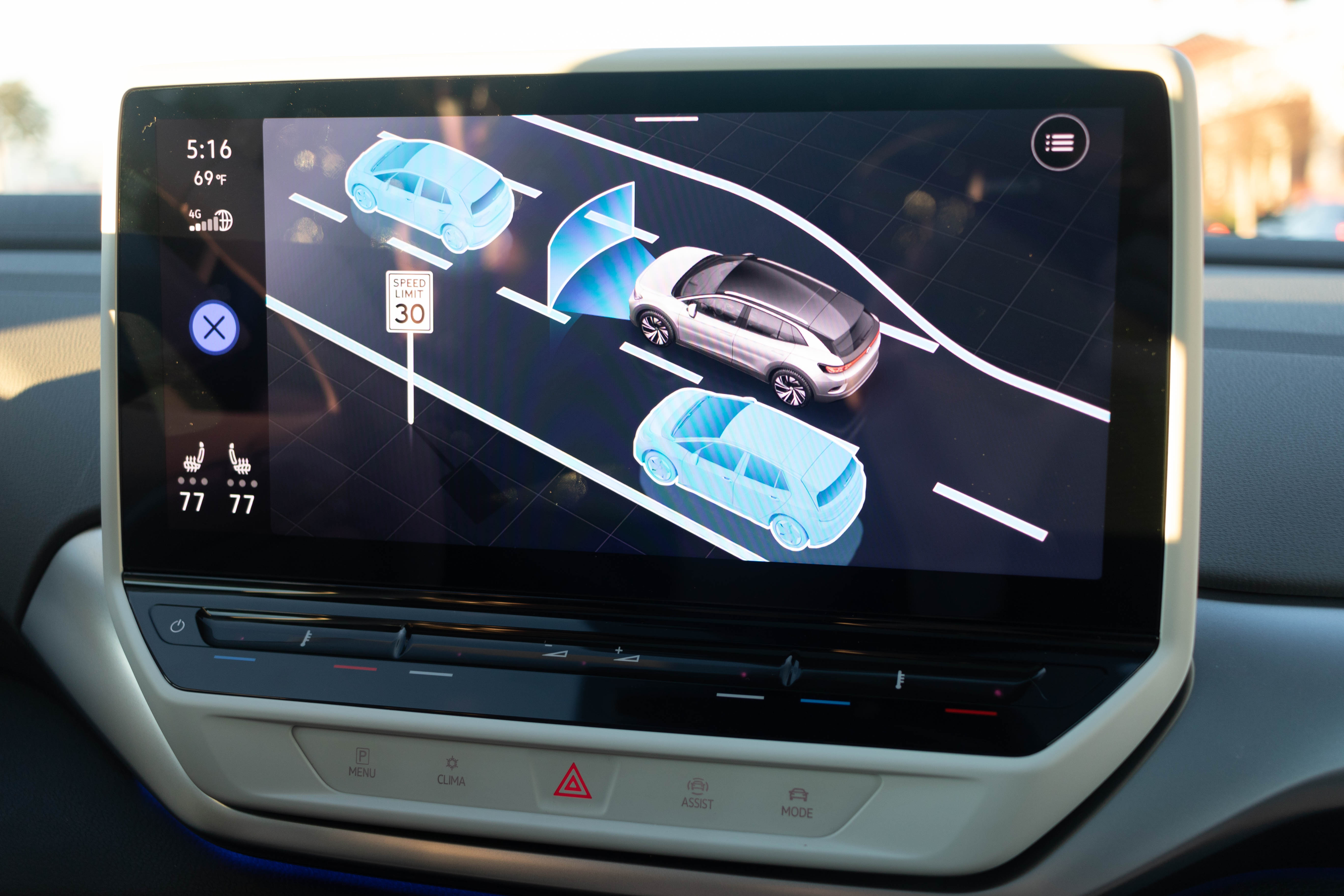
VW’s Travel Assist is the branded name for the company’s Level 2 autonomous driving system, which works at speeds that range from 0-95 mph. Travel Assist uses both the adaptive cruise control and the lane-keeping systems to follow the road and other vehicles ahead. When a motorcycle suddenly hops into your lane, the instrument screen shows an image of a motorcycle directly in front of the vehicle. If said motorcycle decides to randomly slam on the brakes, the ID.4 responds and brakes automatically. If traffic comes to a stop ahead, the ID.4 Travel Assist waits until traffic moves again. It approximates a human response to traffic motion very well–neither waiting inordinately long and leaving huge gaps (which causes rubberbanding in traffic) nor accelerating aggressively.
The system makes long stints in heinous traffic bearable. I spent an hour commuting on the dreaded 405 freeway in Los Angeles during rush hour and only had to keep my hands lightly on the capacitive steering wheel to keep the system engaged.
The skateboard powertrain
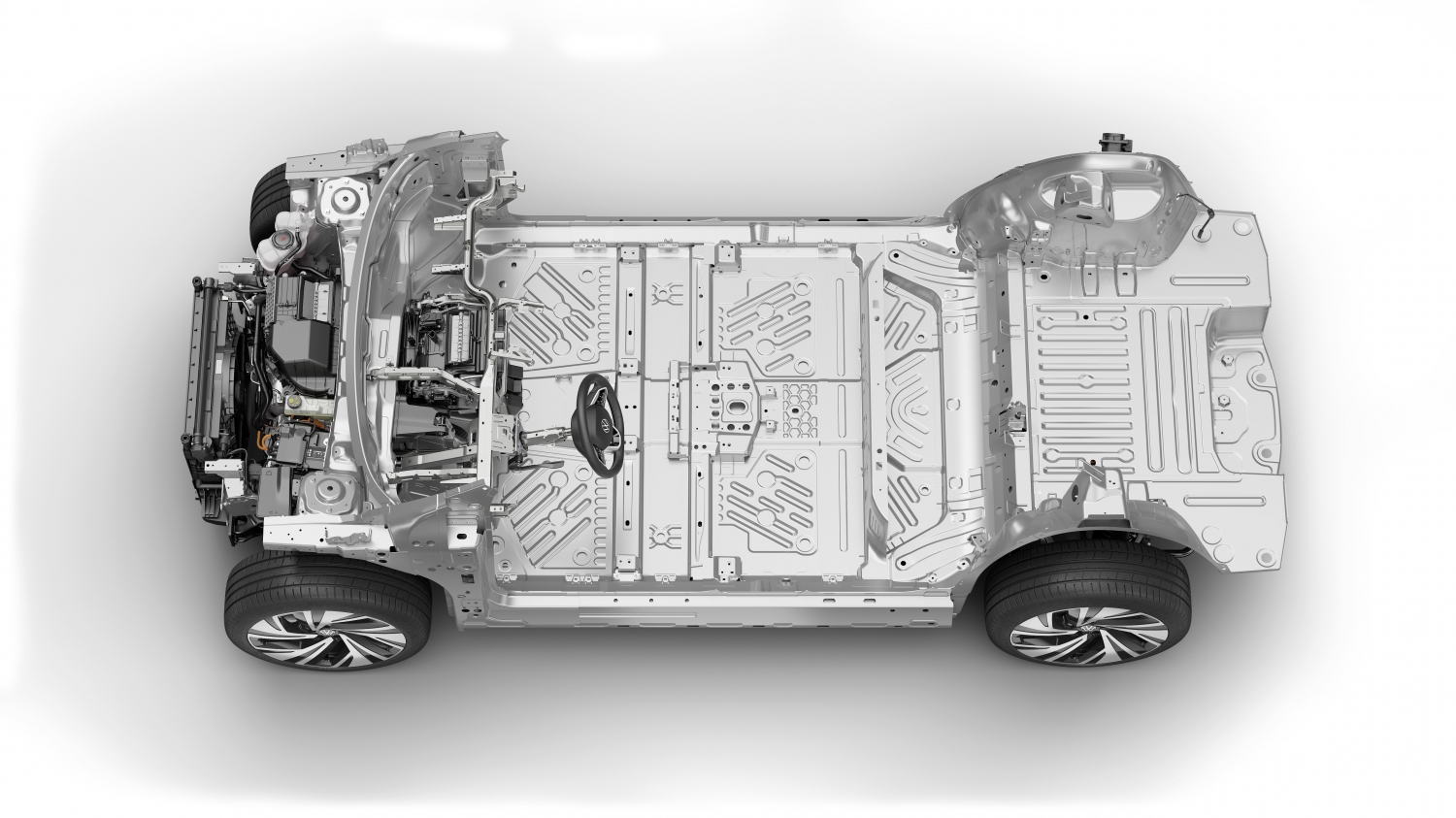
The VW ID.4 is built on a new skateboard architecture called MEB or modular electric drive matrix, with an AC permanent-magnet synchronous motor that makes 201 horsepower and 229 lb-ft of torque mounted at the back of the vehicle, above the rear axle–much like the old Beetle. At launch, VW is only offering a rear-wheel-drive version, but an all-wheel-drive version will be available by the end of the year, offering 302 horsepower.
Volkswagen is purchasing batteries from Panasonic for the ID.4 and assembling the 82-kWh, 12-module, 288-pouch-cell battery packs themselves at plants in China and Germany. There are plans to begin production in the U.S. soon. Volkswagen also builds its own electric motors.
All in, the VW ID.4 makes electric vehicles more attainable for the crossover buying public who can’t afford the high price tags for the other luxury all-electric crossovers like a Jaguar I-Pace, Tesla Model Y, Polestar or Audi E-tron.
Yet it also competes well with popular gasoline-powered crossovers like the Honda CR-V and the Toyota RAV4, especially when you add in the potential for as much as $7500 in rebates. Where the VW ID.4 truly stands out is in its blending of advanced technology and affordability in a good-looking EV, that won’t give you range anxiety. Will it be the “car for the millions?” We’ll have to wait and find out.
The alternative asset market showed promise pre-pandemic but amid a broader rally among traditional asset classes, the number of investors searching for and promoting value in the space has exploded. That has, in turn, promoted a pretty major influx of VC dollars into startups building platforms that wrangle these buyers into specific communities.
Enter, Alt. The young startup has received more than $31 million from top investors intrigued by the particularly hot space it has bulked up its expertise in — physical sports trading cards. The company provides a Goat-like marketplace for the cards, authenticating the transactions and providing buyers with the peace of mind that the slice of cardboard they’re dropping several thousands of dollars on is no fake. While entities like NBA Top Shot have rallied a new generation of buyers around blockchain era digital trading cards, its success has been enabled by the excitement that traditional collectibles markets have been garnering recently.
After years of stocking up on sports trading cards, Alt CEO Leore Avidar is just happy to have more people to talk about his obsession with. Like many in the sports card community, Avidar has spent years collecting cards and engaging with forums online, but it’s been an interest he hasn’t been able to share with friends and family given its somewhat fringe appeal. This isn’t the case today, Avidar says, with old collectors re-entering the market as they dust off aged collections and new collectors intrigued by skyrocketing prices and a more connected online community.
“I’ve talked with a lot of people in the community and one of the things I love is how intergenerational this is, I see a lot of like kids and their parents doing this together,” Avidar tells TechCrunch.
As the market has moved more mainstream, platforms like Alt have also begun seeing more investor interest. In the span of a few months, Alt wrapped a pair of funding rounds from investors hungry to embrace a play in the market — a seed round led by First Round and a Series A led by Reddit co-founder Alexis Ohanian’s new firm Seven Seven Six. Other Alt investors include John and Patrick Collison, Kevin Durant, SV Angel, BoxGroup, Sue Wagner, and Jeff Morris’s Chapter One.
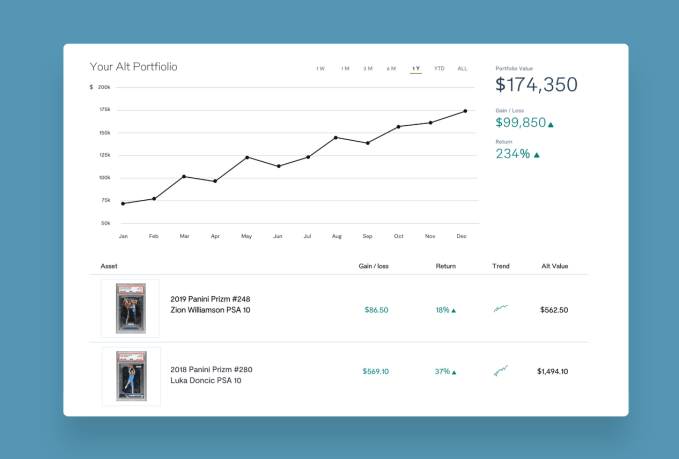
Avidar wants Alt’s platform to increase transparency and liquidity in the alternative assets space and make acquiring assets here just as easy as platforms like Robinhood have made buying and selling stocks. Avidar’s central strategy to capturing this market and bringing it to his platform is by significantly undercutting the fees structure of other sites, with Alt charging 1.5% of the total sales price including processing fees.
In addition to authenticating its stock, Alt has had to build some infrastructure that’s somewhat custom to the trading cards market. Users that are less concerned with holding their physical cards and more worried about them being lost or damaged over time can opt to have Alt store their physical cards in a temperature and light-controlled vault (for a fee), ensuring that physical degradations of the card don’t affect its value. One of Alt’s key features that Avidar expects to be popular with collectors is their Zestimate-like Alt Value rating which will give card buyers and sellers a closer idea of what the market value of their card is based on historic transactions and the trending growth metrics.
The team is launching the Alt market with sports trading cards, but plans to expand its reach to other alternative assets as the marketplace matures further, with Avidar highlighting markets like watches, sneakers and art as potential growth areas.
We’re just a few weeks out from the first TC Early Stage 2021 event on April 1-2. This two-day bootcamp helps early-inning founders develop core entrepreneurial skills for startup success. We’re talking essential topics led by experts in their field.
Case in point. Intellectual property is your bread and butter — you need to safeguard it and understand its value from a VC’s perspective. And while you’re an early-stage founder, it’s never too early to learn the ins and outs of mergers and acquisitions because you don’t ever want to get caught flatfooted — especially if your startup takes rapid flight.
With all that in mind, we’ve lined up a group of heavy hitters — from Perkins Coie, Merus Capital and Brainbase — to share their expertise on M&A and protecting IP. Don’t miss these three interactive breakout sessions with some of the best minds in the business.
Creating and Protecting IP Value in Connection with VC Financings (Perkins Coie)
How do venture capital investors value formal Intellectual Property (IP) rights when deciding to fund a technology or life sciences start-up? How do they conduct IP due diligence? How do investors and founders, post-funding, ensure their start-ups pursue an IP strategy that optimizes exit valuation for all? Perkins Coie partners Michael Glenn (Patent Prosecution) and Matt Oshinsky (Emerging Companies Venture Capital) join a seasoned venture capitalist to discuss these and other questions regarding safeguarding IP rights and maximizing the value of all technology development activities. Brought to you by Perkins Coie.
An M&A Playbook for Startup Founders – Lessons from Google & Microsoft (Merus Capital)
One of the most important decisions a founding team makes is when to consider selling the company to a strategic buyer. In this session, learn how to approach acquirors, avoid common pitfalls and maximize your chances for an eye-popping valuation. Hear from Sean Dempsey, founding partner of Merus Capital, who spent 10 years leading acquisitions for Google and Microsoft, and Dave Sobota, VP of Corporate Development at Instacart, and former M&A leader at Google. Brought to you by Merus Capital.
Naming & Protecting Your Company’s Intellectual Property (Brainbase)
You have an idea for a game-changing product or service — what do you call it? Once you’ve picked a name, how do you make sure nobody else is using it? Is the domain and Twitter handle available? Brainbase makes it easy for anyone to file a trademark without a lawyer, and instantly own your brand across all channels. In this session, company co-founder and CEO, Nate Cavanaugh explains the importance of owning your company’s trademark — both for brand protection and for fundraising due diligence. Brought to you by Brainbase.
Whew, that’s some good stuff right there. And you’ll find plenty more whip-smart presentations in the Early Stage 2021 agenda. Check it out and strategize your day.
TC Early Stage 2021: Operations and Fundraising takes place on April 1-2. Get your pass right here and join your colleagues to learn the best ways to build a startup. Pro tip: Attend both Early Stage 2021 events and double your knowledge. TC Early Stage 2021: Marketing and Fundraising runs July 8-9. Early-bird pricing on dual-event tickets remains in play until March 26 at 11:59 pm (PST). Buy yours before the deadline and save up to $100.
The popularity of video and other streamed content like podcasts is continuing to grow at a breakneck speed, and today a startup called Epidemic Sound, a marketplace to source the background music for that media, is announcing a huge round of funding to scale along with it. The Stockholm-based startup has raised $450 million from Blackstone Group and EQT Growth, an equity round that values Epidemic Sound at $1.4 billion.
Epidemic currently features some 32,000 music tracks and 60,000 sound effects, and the plan will be to continue building out the technology on its platform to provide better tools to creators for matching music to media, to expand that catalogue, to grow its customer base, and to take the service global with more localized offerings.
$450 million may sound like a lot of money for a company that — if you’ll excuse the pun — hasn’t made a lot of noise up to now. But the funding is underpinned with some big ambitions and significant metrics.
“It ties into the size of the vision,” co-founder and CEO Oscar Höglund said in an interview. “We are trying to soundtrack the internet. That’s what it comes down to.”
For an idea of how the startup is growing, when we last covered funding for Epidemic Sound in 2019 (a more modest $20 million at a $370 million valuation), it saw its tracks playing for an average of 250 million hours each month on YouTube alone.
Since then, that figure has grown by more than 400% and is now well over 1 billion hours each month. Höglund says that in terms of streams, YouTube videos using music from Epidemic Sound artists are played 1.5 billion times each day. And that’s before you consider the traffic for Epidemic music used across TikTok, Facebook and Instagram, Snapchat and other platforms.
“The macro trend is exploding,” Höglund said. Counting composers and other creators, there are around 150,000 people using its platform today.
But considering that there are around 37 million YouTube channels, and that’s not counting the many other places like Twitch, TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat and elsewhere that you might find people, there is a lot of room to grow.
“We look for huge open-ended markets, and [in this market] Epidemic is growing into an industry leader,” Jon Korngold, the global head of Blackstone Growth who led on its investment, said in an interview.
Two-sided music marketplace
Epidemic Sound, positions itself as a marketplace, where musicians can upload their recorded tracks, and those who want to use them can come with some ideas in mind of what they’d like to find — music is searchable by genre, mood, instruments, tempo, track length and popularity — and then purchase them with pricing based on where they will be used, not how often they will be heard.
It also offers subscriptions for unlimited use based on personal use ($15/month) or commercial use ($49/month). It’s a formula that helped the startup tip into profitability, although at the moment it’s focused more on growth and is back in red.
Founded back in 2009, Epidemic was started by Höglund and Jan Zachrisson to address a specific gap in the market: their aim was to make it easier, and less legally risky, to add music to digital media. It’s funny to think of it, but 11 years ago, the digital music market was still mostly about downloads, and most of them (95%) were illegal. This report from the IFPI at the time didn’t even seem to mention streaming as a concept.
And to Epidemic’s opportunity, there were also no clear, easy to use marketplaces in existence to make music available, and to buy it under easy licensing terms.
“At the core, Epidemic was and is about the restriction free experience for creators,” said Victor Englesson, a partner and investment advisor at EQT Partners. “That was one of the big pain points for user-generated content, and that has been true since its inception. Epidemic Sound controls 100% of the rights in its library.”
Fast forward to today, and the opportunity is less about offering easy licensing, which now seems to be table stakes, but more directly addressing a huge demand.
In a world where video has proven to be a hugely popular with consumers — Cisco previously estimated that video accounted for some 80% of all internet traffic in 2020, but with those numbers dating from pre-pandemic, I wouldn’t be surprised if it was more — it has also proliferated as a medium for creators. Unsurprisingly, a lot of companies have emerged to provide tools for creators to produce and distribute their video content, and that has included providing them with music.
That has led to a pretty crowded market for soundtracking platforms. Others in the same area include the likes of Artlist (which also provides a catalogue of stills and video; it also raised money last year), Upbeat, and Comma.
Platforms themselves also provide music tools to creators, casual and otherwise, and that has extended far beyond YouTube.
On TikTok, tracks themselves go viral and become earworms overnight. And it’s interesting that Snap last year made a move that points to how it might leverage a role for itself in the music creation and dissemination marketplace. Last year, it quietly acquired an app called Voisy, which lets people overlay and edit their own tunes and vocals over a selection of beats, and then share those creations.
Within all that, Epidemic is more than just a simple platform for exchange, however.
In addition to operating its own platform, Epidemic also partners with other platforms where people are creating content, such as Adobe, Canva, Getty and Lightricks, which offer Epidemic’s music streams as part of their one-stop shops.
And there is also the “brain” behind what Epidemic has built. It tracks which music is used the most, and then how that music plays with audiences, it has been building a gradual picture of the music tastes of the global market — a music graph, as it were — information that it in turn uses to help sort music, match it up better with those looking for it, and to help encourage composers to create further tracks to meet demand.
“Because we collect data and because music leaves a footprint, we can see when there is a huge ask for metal lullabies, for example,” said Höglund. “We can then commission more of that kind of track, and it will get picked up.”
The growth of Spotify, and the massive investments made by Apple, Google, Facebook and others into music streaming, tells a story of how the physical music business has declined but music listening very much has not, a trend only accentuated in the last year, where concerts were cancelled and virtual streaming took their place.
Epidemic is an interesting counterpoint to all of these, focusing not on deals with labels and the Billie’s and Beyonce’s of the world, but a very long tail of creators who may have no deals of the sort in their sights.
While companies like Spotify have turned their attention to building out brands as monetization platforms for artists, that was a part of the equation for the start for Epidemic.
Music creatives receive an upfront payment for each track Epidemic buys, with payment varying depending on the track. It also splits the revenue from streaming platforms where the music might later get played.
The company says that on average musicians can make tens of thousands of dollars year, with a select few making hundreds of thousands of dollars per year. “It’s massive distribution and reach,” he said.
And some grow in their own right, not just as anonymous partners to video creators. Ooyy, Kospy and Loving Caliber are three that have crossed over into their own stardom, so the gap between what Epidemic Sound is doing for musicians and what a platform like, say, Spotify or YouTube might do is not as wide as you might think. (That also also points to some very obvious and formidable competitors — or acquirers or partners — down the line.)
Combined with its size and growth, it’s this engine that has helped Epidemic Sound grow in what has become a pretty crowded market.
“This is, at the end of the day, a data business,” said Korngold at Blackstone Growth.