& meet dozens of singles today!
User blogs
Organizations spend ungodly amounts of money — millions of dollars — on business intelligence (BI) tools. Yet, adoption rates are still below 30%. Why is this the case? Because BI has failed businesses.
Logi Analytics’ 2021 State of Analytics: Why Users Demand Better survey showed that knowledge workers spend more than five hours a day in analytics, and more than 99% consider analytics very to extremely valuable when making critical decisions. Unfortunately, many are dissatisfied with their current tools due to the loss of productivity, multiple “sources of truth,” and the lack of integration with their current tools and systems.
A gap exists between the functionalities provided by current BI and data discovery tools and what users want and need.
Throughout my career, I’ve spoken with many executives who wonder why BI continues to fail them, especially when data discovery tools like Qlik and Tableau have gained such momentum. The reality is, these tools are great for a very limited set of use cases among a limited audience of users — and the adoption rates reflect that reality.
Data discovery applications allow analysts to link with data sources and perform self-service analysis, but still come with major pitfalls. Lack of self-service customization, the inability to integrate into workflows with other applications, and an overall lack of flexibility seriously impacts the ability for most users (who aren’t data analysts) to derive meaningful information from these tools.
BI platforms and data discovery applications are supposed to launch insight into action, informing decisions at every level of the organization. But many are instead left with costly investments that actually create inefficiencies, hinder workflows and exclude the vast majority of employees who could benefit from those operational insights. Now that’s what I like to call a lack of ROI.
Business leaders across a variety of industries — including “legacy” sectors like manufacturing, healthcare and financial services — are demanding better and, in my opinion, they should have gotten it long ago.
It’s time to abandon BI — at least as we currently know it.
Here’s what I’ve learned over the years about why traditional BI platforms and newer tools like data discovery applications fail and what I’ve gathered from companies that moved away from them.
The inefficiency breakdown is killing your company
Traditional BI platforms and data discovery applications require users to exit their workflow to attempt data collection. And, as you can guess, stalling teams in the middle of their workflow creates massive inefficiencies. Instead of having the data you need to make a decision readily available to you, instead, you have to exit the application, enter another application, secure the data and then reenter the original application.
According to the 2021 State of Analytics report, 99% of knowledge workers had to spend additional time searching for information they couldn’t easily locate in their analytics solution.
Abodu, one of a slew of startup companies pitching backyard homes and office spaces to Californians in an effort to help address the state’s housing shortage, has instituted a new “Quickship” program that can take an order from contract to construction and installation in about thirty days.
Behind the quick turnaround time is a pre-approval process that was first rolled out in Santa Fe and came to Los Angeles in recent weeks.
Abodu began installing homes through a pre-approval process back in 2019, when the city of San Jose created a program that allowed developers of alternative dwelling units to submit plans for pre-approval to cut the time for homeowners.
That approval process means that ADU developers like Abodu can be permitted in one hour. Other ADU developers pre-approved in San Jose, Calif. include Acton ADU, the venture backed Connect Homes, J. Kretschmer Architect, Mayberry Workshop, Open Remodel, and prefabADU. In Los Angeles, La Mas, IT House, Design, Bitches, Connect Homes, Welcome Projects and First Office have all had homes pre-approved for construction.
Beyond the cities where Adobu’s ADUs have received pre-approval, the company has built across California in cities ranging from, Palo Alto, Millbrae, Orange County, to LA and Oakland. Units in the Bay Area cost roughly $189,000 as a starting price, compared to the $650,000 to $850,000 it takes to build units in a mid-rise apartment building, or $1 million per unit in a steel-reinforced highrise, according to the company.
“Our Quickship program is the fastest way to add housing,” said John Geary, CEO at Abodu. “Homeowners with immediate needs, be it family situations or those looking for investment income, can now complete an ADU project in as little as four weeks. A key mission for Abodu is to make a serious dent in our state’s housing deficit while providing people and municipalities the necessary blueprint to enact real change. ”
For former TechCrunch writer Kim-Mai Cutler, who serves on the Abodu board of directors the achievement of a 30 day construction milestone is almost a dream come true. Cutler wrote the book (or the equivalent of a book) on the housing crisis and its impact on the Bay Area and California broadly.
That piece led Cutler to work in public service “on boards and commissions overseeing the spending of federal dollars on homelessness and the proceeds of municipal bonds directed at financing affordable housing (because yes, for some segments of residents, you do have to explicitly subsidize housing at the local level.),” as she noted in a blog post about her investment in Abodu.

The interior of an Abodu home. Photo via Abodu.
Cutler backed the company because of her deep knowledge of the issues associated with housing.
“The reason this is a big deal is because Northern California has been the most expensive and unpredictable place to build new housing in the world. Projects typically take several years because of uncertainty with entitlements and materials,” Cutler wrote. “Over the past year, Abodu co-founders John Geary and Eric McInerney have put homes in the backyards of parents bringing kids home from college, a mother-and-son pair that each bought one for their homes in Millbrae, a couple looking to eventually house a grandmother in San Jose and on and on.”
The key inspiration that Abodu’s founders hit on was their concentration on granny flats, casitas and backyard dwellings. “While deliberations over mid-rise density were stalling in Sacramento, the state legislature (and legislatures up north in the Pacific Northwest) were passing bill after bill, including Phil Ting’s AB 68 and Bob Wieckowski’s SB 1069, to make it really easy to add backyard units,” Cutler wrote. “This is the kind of change that suburban America wants, is comfortable with and can politically pass and implement easily.”
To Cutler’s thinking, Adobu’s 30 day construction schedule will change consumer behavior, thanks to the fact that the home can be craned in and installed in less than a day on a foundation constructed in less than two weeks. Its incredibly low cost will enable a lot of opportunities to develop new inventory and the simple fact is that inventory remains a scarce commodity. As Cutler noted, only half as many homes are trading across the United States as were available a year ago, which is happening at the same time as when millennials are entering prime family formation years.
Facebook’s hardware strategy often looks pretty opaque from the outside. The company has done fairly well with Oculus sales amid pandemic demand. Even its Echo Show competitor Portal has seen a bump as people have been forced to socially distance. The company’s smartphone partnership with HTC, meanwhile, fell flat eight or so years back.
Earlier this year, reports surfaced that the company was working on its own Apple Watch competitor. The smartwatch was said to have a health focus, running on an open-source version of Android. That, of course, would mark an interesting alternative from Google’s chosen wearOS.
This week, the company highlighted another wrist-based wearable. The specifics of the project don’t line up super closely with earlier reports, which could well mean two separate projects. Facebook is a big company, after all.
This particular project out of Facebook Reality Labs is more focused on providing an alternative computer interface. Specifically, it seems in line with the company’s augmented reality efforts.
Per yesterday’s blog post:
A separate device you could store in your pocket like a phone or a game controller adds a layer of friction between you and your environment. As we explored the possibilities, placing an input device at the wrist became the clear answer. The wrist is a traditional place to wear a watch, meaning it could reasonably fit into everyday life and social contexts. It’s a comfortable location for all-day wear. It’s located right next to the primary instruments you use to interact with the world — your hands. This proximity would allow us to bring the rich control capabilities of your hands into AR, enabling intuitive, powerful and satisfying interaction.
I will say that, based on the information presented, this seems more conceptual. As in, this could be the key to offering more seamless control for some future augmented reality system. And even still, it’s presented as a step on the way to a more deeply integrated human-computer solution. How deeply you want Facebook to integrate with your neurons is apparently a question we’re all going to have to ask ourselves in the not too distant future.
This interface specifically is designed to use electromyography (EMG) sensors to interpret motor nerve signals and interact with the interface accordingly. The subject interestingly came up during a Clubhouse event featuring Mark Zuckerberg last night. After Pebble founder/YC partner Eric Migicovsky discussed experiences dealing with Apple for his own smartwatch startup, the Facebook CEO said the following:
If you’re trying to build a watch, which we’re exploring as we talked about the wrist thing and I don’t want to call it a watch, but it’s the basic neural interfaces work that our Facebook reality labs team demoed some of our research about today. With the neural interface on the wrist, if you want that to integrate with the phone in any way, it’s just so much easier on Android than iOS. My guess is that this is an area where there probably should be a lot more focus. And I do think the private APIs are just something that makes it really difficult to have a healthy ecosystem.
“Exploring” seems like an operative word here. But it’s always cool/fascinating to see these projects in their early stages. Even if the promises might still seem a tad…overzealous.
EMG will eventually progress to richer controls. In AR, you’ll be able to actually touch and move virtual UIs and objects, as you can see in this demo video. You’ll also be able to control virtual objects at a distance. It’s sort of like having a superpower like the Force.
“Your board will never be the same.”
With that prediction, Nigel Travis, board director and former CEO of Dunkin’ and Papa John’s, kicked off a recent discussion about the future of corporate governance with chief executives and current and aspiring board members.
Just as countless aspects of corporate life have been reshaped over the course of the last year, boards of directors are undergoing significant and lasting transformation. Through our conversations with more than 500 business leaders and work on nearly 300 board searches over the last year, as well as findings from our recent board benchmarking study, we’ve identified five trends in the boardrooms of the United States’ high-growth private companies.
1. Board diversity is imperative
Historically, board members have been tapped from the personal networks of those already in the boardroom. This approach optimizes for trust and convenience at the expense of diversity.
We expect to see continued improvement when it comes to racial and ethnic diversity in the years ahead.
As pressure to diversity the boardroom mounts and societal challenges underscore the risks of the all-male board, companies are starting to take a more inclusive approach to board design. They are reaching outside their networks to appoint women and people of color, discovering that it’s not a pipeline problem — it’s a network problem. In one year’s time, the percentage of late-stage private companies with all-male boards declined from 60% to 49%.
While that’s progress, the fact that nearly half of the most heavily funded venture-backed companies lack a single woman on the board underscores the enormous work still to be done. Today, only 11% of high-growth private company board seats are held by women and only 3% by women of color.
However, we expect to see continued improvement when it comes to racial and ethnic diversity in the years ahead. Demand for Him For Her referrals to female board candidates nearly quadrupled in that last quarter of 2020 compared with a year prior, and among the new directors appointed, a quarter identify as Black or African American.
2. Source candidates from across the entire C-suite
When seeking independent directors, boards have traditionally favored CEO experience. Given the gender imbalance among CEOs, preference for that title instantly tips the scales in favor of male candidates.
As boards look to add women, many have discovered the value of taking a more strategic approach to defining criteria for the next director. Instead of relying on the CEO title as a proxy for the desired qualities, boards now conduct a gap analysis, identifying the mix of key competencies that would be most valuable.
The result: a rich pipeline of executive operators who contribute strategic perspective combined with cutting-edge best practices. In addition to CFOs ready to chair an audit committee, we’ve had requests for operators with go-to-market expertise, product leaders known for driving innovation, and people officers who know how to build corporate culture. We’ve even helped companies seeking, for example, business-savvy doctors, nurses and law-enforcement officers to bring the voice of their customers into the boardroom.
3. Independents come earlier
As CEOs look to add diversity and operating expertise to their boards, many are adding independent directors at an earlier stage. How early? “It’s never too early to have an independent director on the board,” according to Brad Garlinghouse, CEO of Ripple, where the first independent was appointed only a year after the company’s founding.
Over the last year, the percentage of the heavily funded private companies with at least one independent director grew from 71% to 84%, and the percentage of board seats held by independents grew from 20% to 25%, according to the 2020 Study of Gender Diversity on Private Company Boards. Among the board searches we’ve conducted for privately held companies, more than 40% were Series B or earlier.
4. The board Zoom is here to stay
The pandemic drove boards onto screens, but even when health risks are mitigated, many will continue to convene virtually at least some of the time. The last year has caused companies to rethink the role of the physical office, and the importance of the physical boardroom is getting new scrutiny. Though most CEOs and directors will still favor in-person attendance for formal board meetings, we expect a new tolerance for remote participation and an increase in ad-hoc virtual meetings.
Beyond reduced travel and ease of scheduling, there’s a hidden benefit to virtual meetings that leaders would be wise to exploit: the reduced opportunity cost of more attendees. The impact of “another body in the boardroom” has long been an argument against allowing company executives to attend board meetings. We expect that, with a virtual format, CEOs will take advantage of the development opportunity to expose more of their leaders to board discussions.
On the flip side, virtual meetings require a more conscious effort to build relationships. Boards will need to balance the convenience of virtual meetings with the value of in-person interactions in building rapport and fostering collaborative decision-making.
5. Stakeholder capitalism takes root
Propelled by increasing pressure in the public markets and by the growing number of consumers who make value-based purchasing decisions, private company boards will give sustainability more overt consideration in their decision-making. In his annual letter, BlackRock CEO Larry Fink pointed to evidence of a “sustainability premium” for companies that outperform their industry peers on ESG measures. As public companies standardize on metrics and disclosure around ESG performance, that discipline will extend into the boardrooms of companies that aim to compete in the global marketplace.
Private companies drive innovation in nearly every corner of the economy, yet their boardrooms have remained remarkably unchanged over the last several decades. We expect that 2020 will prove to be an inflection point in corporate boardrooms; this period of board transformation will be defined by increased diversity and inclusion and a growing emphasis on sustainable value creation. As these initiatives take root, beneficiaries will include not just the companies and their investors, but employees, customers, suppliers and society at large.
There is a prevailing notion that while the cloud infrastructure market is growing fast, the vast majority of workloads remain on prem. While that could be true, new research from Synergy Research Group found that cloud infrastructure spending surpassed on prem spending for the first time in 2020 — and did so by a wide margin.
“New data from Synergy Research Group shows that enterprise spending on cloud infrastructure services continued to ramp up aggressively in 2020, growing by 35% to reach almost $130 billion. Meanwhile enterprise spending on data center hardware and software dropped by 6% to under $90 billion,” the firm said in a statement.
While the numbers have been trending toward the cloud for a decade, the spending favored on prem until last year when the two numbers pulled even, according to Synergy data. John Dinsdale, chief analyst and research director at Synergy says that this new data shows that CIOs have shifted their spending to the cloud in 2020.
“Where the rubber meets the road is what are companies spending their money on, and that is what we are covering here. Quite clearly CIOs are choosing to spend a lot more money on cloud services and are severely crimping their spend on on-prem (or collocated) data center assets,” Dinsdale told me.
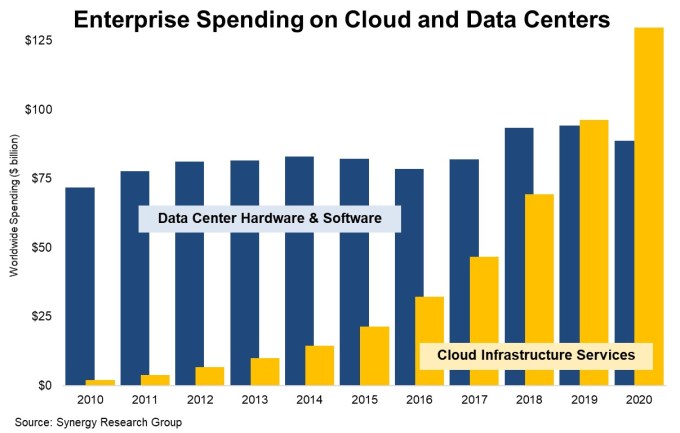
Chart: Synergy Research Group
The total for on prem spending includes servers, storage, networking, security and related software required to run the hardware. “The software pieces included in this data is mainly server OS and virtualization software. Comparing SaaS with on-prem business apps software is a whole other story,” Dinsdale said.
As we see on prem/cloud numbers diverging in this way, it’s worth asking how these numbers compare to research from Gartner and others that the cloud remains a relatively small percentage of global IT spend. As workloads move back and forth in today’s hybrid world, Dinsdale says that makes it difficult to quantify where it lives at any given moment.
“I’ve seen plenty of comments about only a small percentage of workloads running on public clouds. That may or may not be true (and I tend more towards the latter), but the problem I have with this is that the concept of “workloads” is such a fungible issue, especially when you try to quantify it,” he said.
It’s worth noting that the pandemic has led to companies moving to the cloud much faster than they might have without a forcing event, but Dinsdale says that the trend has been moving this way over years, even if COVID might have accelerated it.
Whatever numbers you choose to look at, it’s clear that the cloud infrastructure market is growing much faster now than its on premises counterpart, and this new data from Synergy shows that CIOs are beginning to place their bets on the cloud.