& meet dozens of singles today!
User blogs

The post Let’s Talk About CBD… appeared first on A Practical Wedding: Wedding Planning, Inspiration, and Ideas.
Buying and selling residential real estate is a complex business, no matter where you live. A slew of startups in the United States are focused on streamlining that process for people. But in Brazil, where no MLS exists, the challenge of digitizing real estate is even greater.
One startup that has set out to serve as a “one-stop shop” for Brazilians to help them manage the home buying and selling process has managed to attract one of the largest — if not the largest — funding rounds ever raised by a Brazilian startup.
This morning, digital real estate platform Loft announced it has closed on $425 million in Series D funding led by New York-based D1 Capital Partners. A mix of new and existing investors also participated in the round, including Advent, Altimeter, DST, Silver Lake, Soros, Tarsadia, Tiger Global, Andreessen Horowitz, Caffeinated, Fifth Wall, Monashees, QED and Vulcan, among others.
The round values Loft at $2.2 billion, a huge jump from its being just near unicorn territory in January 2020, when it raised a $175 million Series C.
A round of this size is impressive for any startup, but especially for one that was founded just over three years ago in Latin America. The region has seen explosive growth as of late, with a maturing startup scene in Brazil in particular. São Paulo-based Loft too has seen major growth. While the company was less forthcoming about its financials as of late, it told me last year that it had notched “over $150 million in annualized revenues in its first full year of operation” via more than 1,000 transactions.
In 2020, Loft saw the number of listings on its site increase “10 to 15 times,” according to co-founder and co-CEO Mate Pencz. Today, the company actively maintains more than 13,000 property listings in approximately 130 regions across São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, partnering with more than 30,000 brokers. Not only are more people open to transacting digitally, more people are looking to buy versus rent in the country.
“We did more than 6x YoY growth with many thousands of transactions over the course of 2020,” Pencz told TechCrunch. “We’re now growing into the many tens of thousands, and soon hundreds of thousands, of active listings.”
The company’s revenues and GMV (gross merchandise value) also “increased significantly” in 2020, according to Pencz, who declined to provide more specifics. He did say those figures are “multiples higher from where they were,” and that Loft has “a very clear horizon to profitability.”
“Loft has adapted really fast to the new reality we’re living in, with COVID having only propelled or accelerated our growth,” Pencz said.
Pencz and Florian Hagenbuch founded Loft in early 2018 and today serve as its co-CEOs. The aim of the platform, in the company’s words, is “bringing Latin American real estate into the e-commerce age by developing online alternatives to analogue legacy processes and leveraging data to create transparency in highly opaque markets.” The U.S. real estate tech company with the closest model to Loft’s is probably Zillow, according to Pencz.
In the United States, prospective buyers and sellers have the benefit of MLSs, which in the words of the National Association of Realtors, are private databases that are created, maintained and paid for by real estate professionals to help their clients buy and sell property. Loft itself spent years and many dollars in creating its own such databases for the Brazilian market. Besides helping people buy and sell homes, it offers services around insurance, renovations and rentals.
In 2020, Loft also entered the mortgage business by acquiring one of the largest mortgage brokerage businesses in Brazil. The startup now ranks among the top-three mortgage originators in the country, according to Pencz. When it comes to helping people apply for mortgages, he likened Loft to U.S.-based Better.com.
The startup has also grown its number of employees in the past year, growing from 450 last January to 700 today. In particular, it’s significantly beefed up its tech team, according to Pencz.
Image courtesy of Loft
Notably, at the time of its series C, the investment marked the first and only investment in Latin America for Vulcan Capital (the investment arm of Microsoft co-founder Paul Allen) and the first and only Brazilian investment for Andreessen Horowitz.
This latest financing brings Loft’s total funding raised to an impressive $700 million. Other backers include Brazil’s Canary and a group of high-profile angel investors such as Max Levchin of Affirm and PayPal, Palantir co-founder Joe Lonsdale, Instagram co-founder Mike Krieger and David Vélez, CEO and founder of Brazilian fintech Nubank. In addition, Loft has also raised more than $100 million in debt financing through a series of publicly listed real estate funds.
Loft plans to use its new capital in part to expand across Brazil and eventually in Latin America and beyond. The company is also planning to explore more M&A opportunities.
“We’re now going into this year extremely well-capitalized and I think that in addition to doubling down on the core business, there might be strategic acquisitions also on the horizon,” Pencz told TechCrunch. “We also plan to make Loft as much of a regional and potentially global business, following in the footsteps of some of the other Brazilian companies who recently have been expanding globally.”
Dan Sundheim, founder of D1 Capital, said that part of his firm’s approach as investors is identifying opportunities “at the confluence of structural shifts, secular trends and world-class management teams.”
“Analyzing Loft, we were particularly impressed by the team’s focus and relentless execution, which has allowed them to build scale as well as deep data and technology moats in a short amount of time,” he said in a written statement.
Insuretech startup Counterpart, has raised $10 million in funding led by Valor Equity Partners. Also participating was Susa Ventures and Felicis Ventures. Counterpart works in the ‘management liability’ insurance market. Counterpart will also partner with Markel Specialty, a specialty insurance division of Markel Corporation, to offer its management liability insurance products.
Insuretech startups like Oscar, Lemonade, and Root have made incursions into personal insurance. What has been less prevalent, says Counterpart, is startups tackling the $300bn corporate insurance market.
Counterpart is competing with Next Insurance which has raised $631M, and which also provides small business liability insurance, as well as the big insurance carriers, from AIG to Berkshire Hathaway.
Counterpart is used by some wholesale brokers in the United States to allow small to medium businesses get insurance coverage, because it digitizes much of the process, from application submission, coverage selection, binding, claims management, and loss prevention. Counterpart says this market has become less attractive to insurance carriers because of the increasing claims costs and severity, and their lack of digitization of the process.
Tanner Hackett, founder, and CEO, said in a statement: “The $1.2tn insurance industry is going through a digital revolution.. We saw an outsized opportunity with management liability, a critical insurance line in which we have unique expertise.”
Valor Equity Partners partner and Counterpart board member Jon Shulkin said: “Counterpart’s platform goes beyond the scope of a traditional insurer, layering in insights, tools, and services to help business stakeholders navigate this extremely challenging operating environment.”
Valor was an early backer of Tesla, SpaceX, Addepar, and GoPuff. Susa has previously backed Robinhood, PolicyGenius, and Newfront Insurance. Felicis has funded Hippo, Plaid, and Credit Karma.
Digital identity services — used as a key link between organizations to verify that you are who you say you are online and individuals logging into those services — have come into their own in this past year. The pandemic has precipitated a shift where many services we might have used in person are now accessible via the web and apps, but at the same time, the amount of cybercrime aimed at abusing that environment is on the rise, and both trends fuel a stronger demand for ID verification tools. Now, one of the companies that provides digital identity products is announcing a large round of funding, underscoring both the market size and its ambitions to be a central player in that space.
Jumio, which has built a platform that provides a variety of digital identity tools and technology — using biometrics, machine learning, computer vision, big data, and more to run checks on ID documents, log-ins, suspicious financial activity, prevent identity theft and more — has closed a $150 million round of funding, money that it will use to build more tools available on its platform, and to double down on customer growth after a big year for the company.
Currently, the company’s primary business is B2B: it provides tools to enterprise customers like HSBC to manage digital identity verification. Some of the areas where it will be investing include expanding its AI capabilities to do more anti-money laundering work, and to look at building a B2C product, using the data, tools and network of customers that it has to help individuals better manage their identities online.
“I think the big thing is that the foundation of the internet is identity not anonymity,” said CEO Robert Prigge in an interview, who said the trend of digital transformation has spurred that chane. “It’s been a big shift over the last couple of years. People wanted to originally hide behind anonymity, but now identify is the keystone. Whether it’s online banking or social networks, you need to be able to establish trust remotely.”
Of course, anonymity still is there, just in a different form: data protection regulations are all about making sure that we can stay private if we so choose as we use the tools that are now the norm. That presents the challenge and opportunity for a company like Jumio: how to navigate the push for identity while still providing a way to do that with privacy protections in mind.
The funding is coming from a single investor, Great Hill Partners, which will be joining Centana and Millennium as shareholders in the company. The valuation is not being disclosed but CEO Robert Prigge noted a few details that he believes point to the company’s position right now.
He confirmed that Jumio made $100 million in revenues last year; this is the first money the company has raised in nearly five years after bringing in a modest $16 million in 2016; and this looks to be the largest single round ever raised for a digital identity company.
However, given the market environment and the advances of tech, there has been quite a lot of momentum in the space, and a number of other digital identity and anti-money laundering (AML) prevention startups have been launching, growing and raising money — they include just in the last year ForgeRock ($96 million round), Onfido ($100 million), Payfone ($100 million), ComplyAdvantage ($50 million), Ripjar ($36.8 million) Truework ($30 million), Zeotap ($18 million), Persona ($17.5 million) — so I wouldn’t be surprised if this is not an outlier at the end of the day. Acquisitions like Equifax buying Kount earlier this year, meanwhile, point to encroaching competition from other areas like credit rating agencies.
Jumio is notable among this group for being one of the bigger and older players. Prigge said that currently has around 1,000 customers, including some of the very biggest enterprises like the banking group HSBC, United Airlines and the telecoms operator Singtel, and it is active in 200 countries.
It’s also notable for having developed a platform approach, where it offers a range of different kinds of tools. This is in contrast to many others, which — partly as newer entrants — are focusing on more specific technology or addressing a narrower aspect of what is a pretty complex problem. That said, the company’s earliest work seems to still be the mainstay of what it does. The number of documents that it can “read” to begin the process of verifying users now numbers about 3,500. That has propelled more than 300 million verifications made on Jumio’s platform.
“Almost all vendors verify you are who you say you are, not that it’s really you. That is why the biometrics is so important.
In our case we see it as a holistic onboarding,” Prigge said. “We are one of the only AML and KYC [know your customer] providers.” The AML tools came by way of an acquisition the company made last year, of Beam Solutions.
This funding round, nevertheless, is a big step up for a company that has, in fact, seen a lot of ups and downs.
To be very clear Prigge is very explicit when he says that the Jumio he runs has nothing to do with an older incarnation of the company.
Jumio the first came into existence around a decade ago and raised nearly $40 million in funding from investors like Andreessen Horowitz and Eduardo Saverin as an early player in mobile payments, with technology that could use the camera on a phone to scan cards and IDs to enable the payments. That business ran into a lot of hot water for mis-stating financial results and mostly likely other related things, and eventually it filed for bankruptcy in March 2016. Saverin apparently wanted to buy the business — if only to encourage other buyers to come out of the woodwork — eventually Centana did, at a bargain price of $850,000.
While that took a portion of the business (mainly branding, a business concept and some employees) out of bankruptcy, the legacy Jumio remained in a bankruptcy process is, almost exactly five years to the date, still ongoing, partly because the original founder is being accused of destroying documents needed to finally conclude that mess.
The fact that Great Hill Partners is doing the investing here is notable. It’s mostly a PE firm that has been doing an increasing amount of investing in tech companies, which is part of a bigger trend, where more PE firms are getting involved in rounds for later-stage startups.
“Jumio has an incredible foundation – an expert management team, deep product roadmap and a global reach that is positioning the company for significant growth as the volume of online transactions and interactions, and associated fraud, is reaching record-highs. In particular, we have deep conviction in the company’s AI-enabled identity verification solution Jumio Go and KYC orchestration platform,” said Nick Cayer, partner at Great Hill Partners, in an emailed interview. “Jumio will need to both keep pace with incredible demand for online identity verification services, and of course outlast new and evolving competition in the space. We have strong conviction that Jumio has the right management team, innovative product roadmap and group of supporting investors to maintain leadership in the space.”
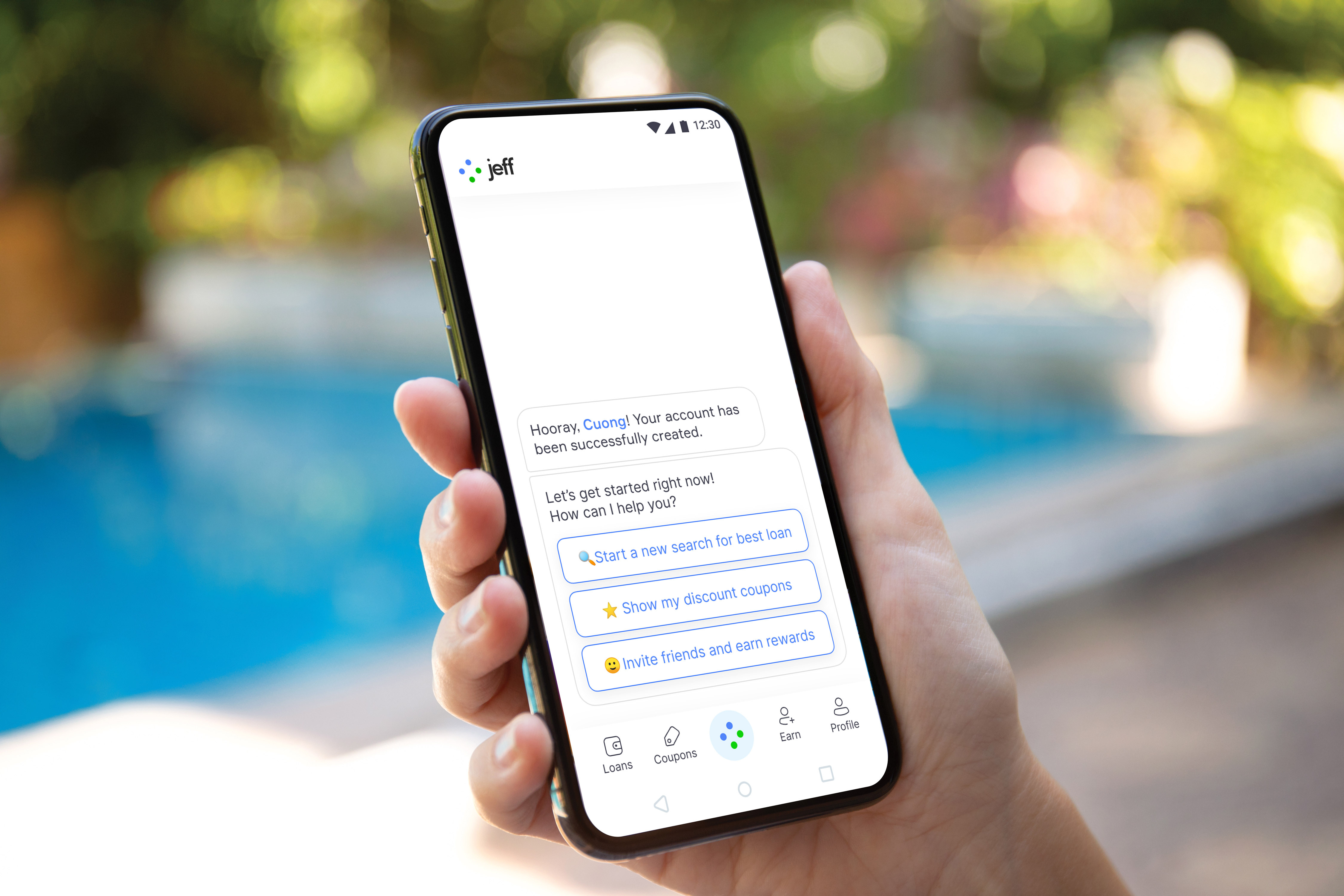
According to the World Bank, more than one billion people in South and East Asia lack access to a bank account. For many, this makes it is difficult to secure loans and other services because they don’t have traditional financial records like a credit score. Jeff’s loan brokerage platform was created to make it easier for financial service providers to integrate alternative data scoring, allowing them reach more potential borrowers.
The startup, which launched its app in Vietnam last year, announced today it has raised $1 million, led by the Estonian Business Angels Network (EstBAN). The funding will be used to enter other Southeast Asian markets, including Indonesia and the Philippines, and introduce new products, like free credit score and insurance offers, digital discount coupons and mobile wallet cashbacks. Other participants in the round included Startup Wise Guys; Taavi Tamkivi, the founder of Salv who formerly held lead roles at TransferWise and Skype; and angel investors from European on-demand ride platform Bolt.
Jeff currently claims more than 300,000 users in Vietnam. Though it is based in Latvia, Jeff will continue focusing on unbanked people in South and Southeast Asia, said founder and chief executive officer Toms Niparts. Its goal is to build a “super app” that combines personalized loan comparisons with other services like e-commerce, mobile top-ups and online discounts, Niparts told TechCrunch in an email.
Before starting Jeff, Niparts was CEO of Spain for Digital Finance International, a fintech company that is part of the Finstar Financial Group, which has investments in more than 30 countries. This gave Niparts the chance to “learn about the similarities and differences of financial services from the inside in different markets,” he said.
In particular, he saw that in Southeast Asian countries, most loan applicants “were rejected not because of bad credit history, low income or other similar reasons, but because there was not enough data about them.” While some lending companies have developed pilot projects for alternative data scoring, the process is often time-consuming, complicated and expensive.
“This is a massive problem in a big part of the world, and it makes absolute sense to build it as a centralised solution,” Niparts said.
In Vietnam, Jeff currently has between 12 to 15 active partners at a time (the number changes because lenders occasionally turn off demand, a standard industry practice), and is adding another eight to 10. In total, the company now has about 80 to 100 potential partners in its Vietnam pipeline, and part of its new funding will be used to expand its team to speed up the onboarding process.
In Indonesia, Jeff has identified about 40 potential partners, “but so far we have only been scratching the surface,” said Niparts. “The Indonesian market is considerably larger than what we have seen in Vietnam, and the forecast is we will grow the pipeline to 150-200 banks and partners in 2021.”
The company’s selling point hinges on its ability to accurately measure creditworthiness based on alternative data. For lenders, this means more pre-qualified leads and access to a larger customer segment.
“Building a credit score is a never-ending process, and we are at the very early stages of it. What we have right now is mainly around publicly accessible information and client-consented data,” Niparts said. This includes behavioral analytics, smart devices meta data, data from social media and other sources that have open APIs.
As Jeff grows, it also plans to make partnerships with mobile wallets, telecom companies and consumer apps. It is developing a lender toolkit that includes bank portal and lender API to reduce the amount of time needed to integrate with the app.
Borrowers sign up for Jeff with the app’s chatbot and can start getting offers once they enter basic information like their name, contact information, the amount they want to borrow and the purpose of the loan. But adding more details and data sources to their profiles, which are screened by multiple lenders at once, increases their chances of approval, and unlocks more offers. This may include uploading documents, connecting social media accounts or consenting to share their smart device metadata.
“As we evolve, new integrations and compatible accounts from other service providers—such as utilities, food delivery, and more—will be regularly added,” said Niparts.
Jeff’s partners currently offer near-prime, peer-to-peer and digital lending services that include unsecured consumer loans, installment loans and motorbike financing. It plans to add more loan products, and is also working on its first insurance collaborations, credit cards and other bank-grade products.
“Our ambition for Jeff is to become a super app, where people can not only get access to financial services that were previously unavailable to them, but also tap in other benefits and discounts,” Niparts said. “This is also a great way to learn more about creditworthiness and what’s on demand. Every new interactions gives us more data and insights to further evolve the accuracy and value added of Jeff’s credit score.”
The number of fintech startups focused on financial inclusion is on the rise across Southeast Asia. Jeff’s competitors fall into two main categories. The first are comparison portals like TopBank, TheBank and GoBear (which recently announced it is closing), that allow users to compare financial providers and banks, but don’t focus on enabling them to access services. The second are companies like CredoLab, Seon and Kalap that provide third-party services like single data-source insights and fraud prevention, but “do not have control over the customer journey,” Nipsart said.
Jeff’s goal is to “be a one-stop shop for both,” he added. “We provide both clients, as well as deeper insights about them for banks and other partners using our platform. At the same time, we are the main point of interaction for the users, which not only solves the main need of comparing financial services and accessing them, but also offers an increasing range of other discounts and benefits.”