& meet dozens of singles today!
User blogs
We’ve seen a lot of trend lines moving throughout 2020 and into 2021 around automation, workflow, robotic process automation (RPA) and the movement to low-code and no-code application building. While all of these technologies can work on their own, they are deeply connected and we are starting to see some movement towards bringing them together.
While the definition of process automation is open to interpretation, and could include things like industrial automation, Statista estimates that the process automation market could be worth $74 billion in 2021. Those are numbers that are going to get the attention of both investors and enterprise software executives.
Just this week, Berlin-based Camunda announced a $98 million Series B to help act as a layer to orchestrate the flow of data between RPA bots, microservices and human employees. Meanwhile UIPath, the pure-play RPA startup that’s going to IPO any minute now, acquired Cloud Elements, giving it a way to move beyond RPA into API automation.
Not enough proof for you? How about ServiceNow announcing this week that it is buying Indian startup Intellibot to give it — you guessed it — RPA capabilities. That acquisition is part of a broader strategy by the company to move into full-scale workflow and automation, which it discussed just a couple of weeks ago.
Meanwhile at the end of last year, SAP bought a different Berlin process automation startup, Signavio, for $1.2 billion after announcing new automated workflow tools and an RPA tool at the beginning of December. Microsoft is in on it too, having acquired process automation startup Softmotive last May, which it then combined with its own automation tool PowerAutomate.
What we have here is a frothy mix of startups and large companies racing to provide a comprehensive spectrum of workflow automation tools to empower companies to spin up workflows quickly and move work involving both human and machine labor through an organization.
The result is hot startups getting prodigious funding, while other startups are exiting via acquisition to these larger companies looking to buy instead of build to gain a quick foothold in this market.
Cathy Tornbohm, Distinguished Research Vice President at Gartner, says part of the reason for the rapidly growing interest is that these companies have stayed on the sidelines up until now, but they see an opportunity and are using their checkbooks to play catch up.
“IBM, SAP, Pega, Appian, Microsoft, ServiceNow all bought into the RPA market because for years they didn’t focus on how data got into their systems when operating between organizations or without a human. [Instead] they focused more on what happens inside the client’s organization. The drive to be digitally more efficient necessitates optimizing data ingestion and data flows,” Tornbohm told me.
For all the bluster from the big vendors, they do not control the pure-play RPA market. In fact, Gartner found that the top three players in this space are UIPath, Automation Anywhere and Blue Prism.
But Tornbohm says that, even as the traditional enterprise vendors try to push their way into the space, these pure-play companies are not sitting still. They are expanding beyond their RPA roots into the broader automation space, which could explain why UIPath came up from its pre-IPO quiet period to make the Cloud Elements announcement this week.
Dharmesh Thakker, managing partner at Battery Ventures, agrees with Tornbohm, saying that the shift to the cloud, accelerated by COVID-19, has led to an expansion of what RPA vendors are doing.
“RPA has traditionally focused on automation-UI flow and user steps, but we believe a full automation suite requires that ability to automate processes across the stack. For larger companies, we see their interest in the category as a way to take action on data within their systems. And for standalone RPA vendors, we see this as validation of the category and an invitation to expand their offerings to other pillars of automation,” Thakker said.
The activity we have seen across the automation and workflow space over the last year could be just the beginning of what Thakker and Tornbohm are describing, as companies of all sizes fight to become the automation stack of choice in the coming years.
Early Stage is the premier ‘how-to’ event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear first-hand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company-building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in – there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion. Use code “TCARTICLE” at checkout to get 20 percent off tickets right here.
Google’s latest investment in India is a startup that is helping businesses come online.
One-year-old DotPe, a Gurgaon-based startup, said on Friday it has raised $27.5 million in its Series A financing round. The round was led by PayU, with participation from existing investor Info Edge Ventures and Google.
The young startup, now valued at about $90 million, helps brick and mortar stores sell to customers online and collect payments digitally.
It’s a problem that scores of startups in India are solving today, but DotPe has some additional hooks. It helps merchants scan their inventories and quickly establish a log online.
Once the catalog is ready, a business can then make it available on WhatsApp and reach customers there. WhatsApp is the most popular smartphone app in India with over 450 million users. DotPe says it also helps businesses get visibility on Google Search.
The startup, co-founded by Shailaz Nag, formerly co-founder and managing director of PayU, also enables neighborhood stores to collect payments from walk-in customers and features tools to offer loyalty points and discounts to customers to boost engagement.
“This new partnership will empower businesses to be more discoverable, expand business avenues and conduct commerce like never before,” said Nag. “Pandemic or not, we are here to reimagine the way offline businesses work and bring the digital revolution to the doorstep of every entrepreneur.”
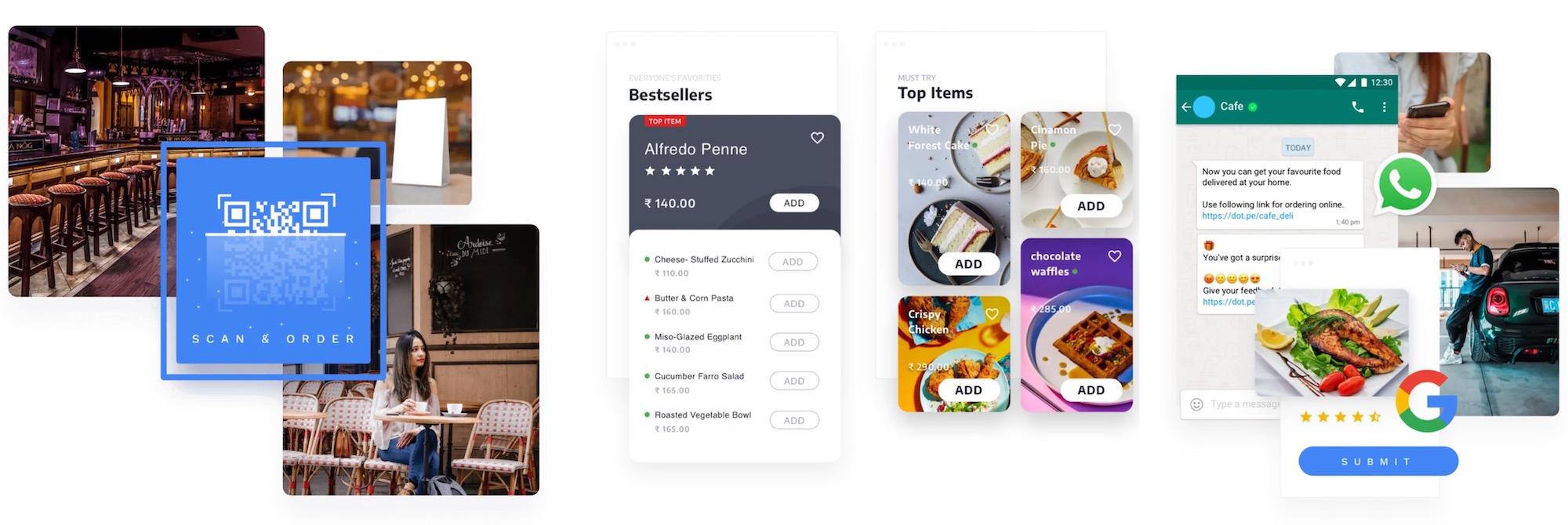
DotPe says its platform, which doesn’t require businesses to install an app, has amassed over 5 million merchants in the last six months. These merchants are seeing over 38% of daily orders from repeat customers, the startup said.
“In a very short time, DotPe has acquired a promising merchant base with its impeccable product experience and innovation,” said Anirban Mukherjee, CEO, PayU India.
Sanjay Gupta, VP and Country Head of Google India, said in a statement that the company’s investment in DotPe is illustrative of Google’s belief in “working with India’s start-up ecosystem towards the goal of building a more inclusive digital economy that will benefit everyone.”
Google announced a $10 billion fund for India last year, its biggest market by users. The Android-maker has invested in several startups in the country including hyperlocal delivery firm Dunzo, InMobi Group’s Glance, and DailyHunt.
DotPe said it will deploy the fresh capital to reach more merchants in India and scale its technology stack to meet the growing demand.
If you browse Instagram, you are probably familiar with the term “link in bio.” Links aren’t allowed in post captions, and users are only allowed one URL in their bios, so many create a simple website with multiple links for their followers. Linktree, one of the most popular “link in bio” services with more than 12 million users, announced today it has raised $45 million in Series B funding. The round was co-led by Index Ventures and Coatue, with participation from returning investors AirTree Ventures and Insight Partners.
Coatue chairman Dan Rose will join Linktree’s board of directors. The Sydney, Australia-based startup’s last round was a $10.7 million Series A announced in October 2020. Linktree’s latest funding will be used on tools that make social commerce easier.
Linktree says about a third, or 4 million, of its users signed up within the last three months. This is in partly because people have been spending more time on social media and e-commerce shopping during the pandemic.
Founded in 2016, Linktree now competes with a roster of “link in bio” services, including Shorby, Linkin.bio and the recently launched Beacons.
“When we launched Linktree, we created an entirely new category. We were first to market and, with over 12 million users globally, still hold 88% of market share,” founder and chief executive officer Alex Zaccaria told TechCrunch. “Inevitably we’ve seen plenty of competitors pop up as a result, but part of the uniqueness of Linktree is its deceptively simple design.”
Zaccaria added that one of Linktree’s differentiators is its adoption by users in a wide range of categories, including health and wellness, real estate, sports, music, politics, publishing and food. It’s used for bio links by Shopify, Facebook, TikTok, YSL, HBO and Major League Baseball, and celebrities like Jonathan Van Ness, Jamie Oliver and Pharrell.
“We might have started as a link-in-bio tool, but over time Linktree has evolved and the platform has become a social identity layer of the internet. Our vision for how the platform will sit at the intersection of digital self-expression and action means we’re thinking boldly when it comes to our roadmap.”
The pandemic’s impact on the business world encouraged adtech startups and digital marketing agencies to collaborate more, helping brands survive the pandemic by bringing businesses closer to consumers.
Although overall spending on advertising slowed in 2020, it is expected to recover in 2021 and reach $630 billion in 2024. According to Statista, North America spends the most on advertising, with second place going to Asia and Western Europe. The rest of Europe, Africa and the Middle East lag behind.
Although overall spending on advertising slowed in 2020, it is expected to recover in 2021 and reach $630 billion in 2024.
However, the Middle East embodies great potential. According to Statista, it boasts the highest growth, with a 600% increase in digital advertising in the MENA region between 2010 and 2015. Although consumers in the region used to prefer traditional advertising channels, the internet took over in 2020, with 44.2% of the total ad expenditures, while TV dropped to 30%.
Here are several essential characteristics of digital advertising in the Middle East region:
- According to a PwC report, 39% of shoppers in the Middle East use social media to find inspiration for purchases, compared to the global average of 29%.
- Due to the existence of a shadow economy, political regulations and unofficial business, the amount of digital ad spending in the MENA region ranged from $1 billion to $1.2 billion in 2020.
- Paid social is the leading category in digital advertising expenditures in the MENA region. Saudi Arabia and Egypt are the largest in terms of active YouTube users.
- There are more than 500 digital agencies listed in the region. UAE is leading in terms of big advertising agencies, while Egypt and Saudi Arabia are famous for small- and medium-size agencies. Most digital marketing talent and creative resources reside in Egypt, Lebanon and Jordan, while most adtech startups are born in Israel, UAE and Qatar, according to digital marketing consultant Yasser Ahmad.
- E-commerce is driving growth, hitting $17 billion in the Middle East in 2020, according to Statista, with many online shoppers increasing the frequency of purchases during the pandemic.