& meet dozens of singles today!
User blogs
Not every company’s founders find themselves on a first name basis with the local bomb squad, but then again not every company is Noya Labs, which wants to turn the roughly 2 million cooling towers at industrial sites and buildings across the U.S. into CO2 sucking weapons in the fight against global climate change.
When the company first started developing prototypes of its devices that attach to water coolers, the company’s founders, Josh Santos and Daniel Cavero, did what all good founders do, they started building in their backyard.
The sight of a 55 gallon oil drum, a yellow refrigeration tank in a sous vide bath attached to red and blue cables didn’t sit so well with the neighbors, so Santos and Cavero found themselves playing host to the bomb squad multiple times, according to the company’s chief executive, Santos.
“We proved that it could capture CO2, and we achieved something that no startup should achieve,” Santos said of the dubious bomb squad distinction.
Santos and Cavero were inspired to begin their experiments with direct air capture by an article describing some research into plants’ declining ability to capture carbon dioxide that Santos read on the Caltrain on his way to work back in 2019. That article spurred the would-be entrepreneur and his roommate to get to work on experimenting with carbon chemistry.
Their first product was a consumer air purifier that would pull carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in homes and capture it. Homeowners could then sell the captured gases to Santos and Cavero who would then resell it. But the two quickly realized that the business model wasn’t economical, and went back to the drawing board.
They found their eventual application in industrial cooling towers, which the company’s tech can turn into CO2 capturing devices that have the capacity to take in between half a ton and a ton of carbon dioxide per day.
Noya’s tech works by adding a blend of CO2 absorbing chemicals to the water in the cooling towers. They then add an attachment to the cooling tower that activates what Santos called a regeneration process to convert the captured CO2 back into gas. Once they have captured the CO2 the company will look to resell it to industrial Co2 consumers.
It’s not green yet, at least not exactly, because that CO2 is being recirculated instead of sequestered, but Santos said it’s greener existing sources of the gas, which come from ammonia and ethanol plants.
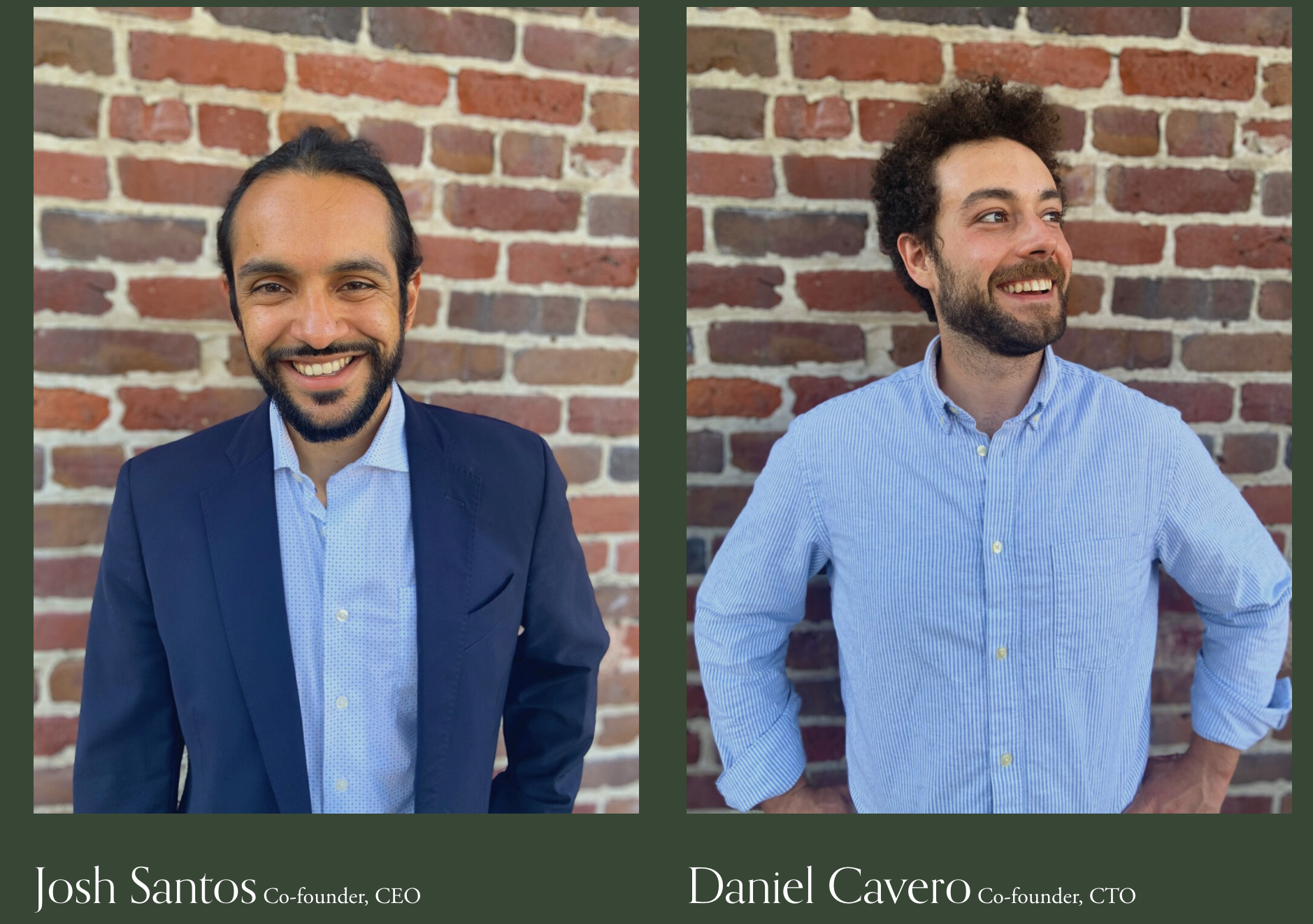

Noya Labs co-founders Josh Santos and Daniel Cavero. Image Credit: Noya Labs
“Five years from now we fully intend to have vertically integrated carbon capture and sequestration. Our first step is locally produced low cost atmospherically captured CO2,” said Santos. “If we were to go all in on a carbon capture that would require a lot of time for us to develop. What this initial model allows us to do is fine tune our capture technology while building up longterm to go to market.”
Santos called it the “Tesla roadster approach” so that the company can build up capital and get revenue and prove one piece of it as an MVP so they can prove other steps of it down the line.
Noya Labs already is developing a pilot plant with the Alexandre Family Farm that should capture between the estimated half a ton and one ton target.
To develop the initial pilot and build out its team, the company has managed to raise $1.2 million from the frontier tech investment firm Fifty Years, founded by Ela Madej and Seth Bannon, and Chris Sacca’s Lowercarbon Capital (whose mission statement to invest in companies that will buy time to “unf*ck the planet” might be one of the greatest). The company’s also in Y Combinator.
“One of the things that makes us excited about this technology is that in the U.S. alone there are 2 million cooling towers. Looking conservatively — if our initial pilot plant can capture 1 ton per day — we’re at right over half a gigaton of CO2 capture.”
And companies are already raising their hands to pick up the CO2 that Noya would sell on the market. There’s a growing collection of startups that are using CO2 to make products. These companies range from the slightly silly, like Aether Diamonds, which uses CO2 to make… diamonds; to companies like Dimensional Energy or Prometheus fuels, which make synthetic fuels with CO2, or Opus12, which uses CO2 in its replacements for petrochemicals.
Prices for commercial CO2 range between $125 per ton to $5,000 per ton, according to Santos. And Noya would be producing at less than $100 per ton. Current Direct Air Capture companies sell their CO2 from somewhere between $600 to $700 per ton.
Stoya’s first installation could cost around $250,000, Santos said. For Bannon, that means the company passes his “Mr. Burns test.”
Introducing "the Mr Burns test" for sustainability companies.
Build a product that Mr Burns (the prototypic self-absorbed egoistic greedy capitalist) would buy not because it's sustainable but because it's the best / cheapest / most convenient.
That's the
to impact at scale.
— Seth Bannon
(@sethbannon) January 6, 2020
“We’ve been digging into the DAC space but haven’t liked the techno-economics we’ve seen. Previous approaches have had too much capex and opex and not enough revenue potential,” Bannon wrote in an email. “That’s what Noya has solved. By leveraging existing industrial equipment, their model is profitable. And better yet, they make their carbon capture partners money, allowing them to scale this up fast. This creates an opportunity to profitably remove 1 gigaton plus a year.”
Over the past year, the coronavirus crisis has spurred app usage in the United States as people stay indoors to limit contact with others. Mobile games particularly have enjoyed a boom, and among them, games from Chinese studios are gaining popularity.
Games released on the U.S. App Store and Google Play Store raked in a total of $5.8 billion in revenue during the fourth quarter, jumping 34.3% from a year before and accounting for over a quarter of the world’s mobile gaming revenues, according to a new report from market research firm Sensor Tower.
In the quarter, Chinese titles contributed as much as 20% of the mobile gaming revenues in the U.S. That effectively made China the largest importer of mobile games in the U.S., thanks to a few blockbuster titles. Chinese publishers claimed 21 spots among the 100 top-grossing games in the period and collectively generated $780 million in revenues in the U.S., the world’s largest mobile gaming market, more than triple the amount from two years before.
Occupying the top rank are familiar Chinese titles such as the first-person shooter game Call of Duty, a collaboration between Tencent and Activision, as well Tencent’s PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds. But smaller Chinese studios are also quickly infiltrating the U.S. market.
Mihoyo, a little-known studio outside China, has been turning heads in the domestic gaming industry with its hit game Genshin Impact, a role-playing action game featuring anime-style characters. It was the sixth-most highest-grossing mobile game in the U.S. during Q4, racking up over $100 million in revenues in the period.
Most notable is that Mihoyo has been an independent studio since its inception in 2011. Unlike many gaming startups that covet fundings from industry titans like Tencent, Mihoyo has so far raised only a modest amount from its early days. It also stirred up controversy for skipping major distributors like Tencent and phone vendors Huawei and Xiaomi, releasing Genshin Impact on Bilibili, a popular video site amongst Chinese youngsters, and games downloading platform Taptap.
Magic Tavern, the developer behind the puzzle game Project Makeover, one of the most installed mobile games in the U.S. since late last year, is another lesser-known studio. Founded by a team of Tsinghua graduates with offices around the world, Magic Tavern is celebrated as one of the first studios with roots in China to have gained ground in the American casual gaming market. KKR-backed gaming company AppLovin is a strategic investor in Magic Tavern.
Other popular games in the U.S. also have links to China, if not directly owned by a Chinese company. Shortcut Run and Roof Nails are works from the French casual game maker Voodoo, which received a minority investment from Tencent last year. Tencent is also a strategic investor in Roblox, the gaming platform oriented to young gamers and slated for an IPO in the coming weeks.
Source: https://techcrunch.com/2021/02/24/chinese-games-us-boom/
BigCommerce has partnered with Walmart to allow its customers to sell on the Bentonville, Arkansas-based retailer’s ecommerce marketplace, it announced this morning. Shares of Austin-based BigCommerce rose sharply in pre-market trading after the news, gaining around 10% before the bell.
Walmart, best-known for in-person shopping, has proven an ecommerce success story in recent years. For example, in its most recent quarter while Walmart as a whole grew 7.3%, its ecommerce sales advanced 69%.
BigCommerce has also reported strong growth in recent quarters, supported in part by partnerships similar to the one that it announced today. The ecommerce SaaS provider rolled out an integration with Wish last year, for example.
In a call concerning its earnings, which were announced before the Walmart news was announced, BigCommerce CEO Brent Bellm told TechCrunch that his company had been impressed with customer uptake of the Wish integration. Regarding the Walmart partnership, in a second interview Bellm told TechCrunch that it was overdue on the BigCommerce side; given the historical success of the Wish deal, it will be curious to dig into how many of the ecommerce platform’s customers opt to sell on Walmart, and how quickly they do so.
TechCrunch also spoke with Walmart exec Jeff Clementz about the arrangement. He stressed Walmart’s online customer monthly-actives — 120 million, per his company — and the breadth of their demand; BigCommerce customers selling on Walmart could expand its product diversity, helping the traditionally physical retailer possible continue its rapid growth.
The two companies are incentivizing adoption of the deal amongst BigCommerce customers by waiving certain fees for a month for retailers that sign up to sell on Walmart; Clementz described it as the first time that his company had offered a “new-seller discount.”
TechCrunch has had its eye on BigCommerce for some quarters now, thanks in part to its 2020 IPO. But the company is also interesting as its regular earnings results provide a lens into the world of ecommerce growth amongst independent digital retailers. Shopify, a chief BigCommerce rival, provides a similar view into the ecommerce world.
Shopify previously integrated with Walmart in the middle of 2020.
Looking ahead, it will be interesting to see if the Walmart partnership helps BigCommerce continue its improving revenue growth. The company is in a marketshare race with Shopify. But while BigCommerce’s rival has posted impressive growth from its integrated solutions, like its payments service, the Austin-based company stresses what it calls a more open model. Shopify charges many customers a percentage of their transaction volume for using a third-party payment solution over its own, for example, which Bellm described as a “tax” during an interview.
“Merchant Solutions” revenue at Shopify, which it generates “principally” from “payment processing fees from Shopify Payments,” grew 116% in 2020 to a little over $2 billion.
So with BigCommerce collecting a partnership with Walmart to match Shopify’s own, we’re seeing not merely two ecommerce platforms go toe-to-toe on providing their customers with as much market access as they can, but two different business philosophies compete. Akin to Microsoft Teams and Slack, it’s a competition to spectate.
Source: https://techcrunch.com/2021/02/24/bigcommerce-customers-can-now-sell-on-walmarts-online-marketplace/
The concept of the “marketing cloud” — sold by the likes of Salesforce, Oracle and Adobe — has become a standard way for large tech companies to package together and sell marketing tools to businesses that want to improve how they use digital channels to grow their business.
Some argue, however, that “cloud”, singular, might be a misnomer: typically those tools are not integrated well with each other and effectively are run as separate pieces of software. Today a startup called Blueshift — which claims to offer an end-to-end marketing stack, by having built it from the ground up to include both traditional marketing data as well as customer experience — is announcing some funding, pointing to the opportunity to build more efficient alternatives.
The startup has closed a round of $30 million, a Series C that co-founder and CEO Vijay Chittoor said it will be using to expand to more markets (it’s most active in the U.S. and Europe currently) and also to expand its technology.
“The product already has a unified format, to ingest data from multiple sources and redistribute that out to apps. Now, we want to distribute that data to more last-mile applications,” he said in an interview. “Our biggest initiative is to scale out the notion of us being not just an app but a platform.”
The company’s customers include LendingTree, Discovery Inc., Udacity, BBC and Groupon, and it has seen revenue growth of 858% in the last three years, although it’s not disclosing actual revenues, nor valuation, today.
The round is being led by Fort Ross Ventures, with strong participation also from Avatar Growth Capital. Past investors Softbank Ventures Asia (which led its last round of $15 million), Storm Ventures, Conductive Ventures and Nexus Venture Partners also invested.
The concept for Blueshift came out of Chittoor’s direct experience at Groupon — which acquired his previous startup, social e-commerce company Mertado — and before that a long period at Walmart Labs — which Walmart rebranded after it acquired another startup where Chittoor was an early employee, semantic search company Kosmix.
“The challenges we are solving today we saw first hand as challenges our customers saw at Groupon and Walmart,” he said. “The connected customer journey is creating a thousand times more data than before, and people and brands are engaging across more touchpoints. Tracking that has become harder with legacy channel-centric applications.”
Blueshift’s approach for solving that has been, he said, “to unify the data and to make decisions at customer level.”
That is to say, although the customer experience today is very fragmented — you might potentially encounter something about a company or brand in multiple places, such as in a physical environment, on various social media platforms, in your email, through a web search, in a vertical search portal, in a marketplace on a site, in an app, and so on — the experience for marketers should not be.
The company addresses this by way of a customer data platform (CDP) it markets as “SmartHub.” Designed for non-technical users although customizable by engineers if you need it to be, users can integrate different data feeds from multiple sources, which then Blueshift crunches and organises to let you view in a more structured way.
That data can then be used to power actions in a number of places where you might be setting up marketing campaigns. And Chittoor pointed out — like other marketing people have — that these days, the focus on that is largely first-party data to fuel that machine, rather than buying in data from third-party sources (which is definitely part of a bigger trend).
“Our mission is to back category-leading companies that are poised to dominate a market. Blueshift clearly stood out to us as the leader in the enterprise CDP space,” said Ratan Singh of Fort Ross Ventures in a statement. “We are thrilled to partner with the Blueshift team as they accelerate the adoption of their SmartHub CDP platform.” Singh is joining Blueshift’s board with this round.