& meet dozens of singles today!
User blogs
The highest court in the land has a lot to say about tech this week. The Supreme Court weighed in on Google’s long legal battle with Oracle on Monday, overturning a prior victory for the latter company that could have resulted in an $8 billion award.
In a 6-2 decision, the court ruled that Google didn’t break copyright laws when it incorporated pieces of Oracle’s Java software language into its own mobile operating system. Google copied Oracle’s code for Java APIs for Android, and the case kicked off a yearslong debate over the reuse of established APIs and copyright.
In 2018, a federal appeals court ruled that Google did in fact violate copyright law by using the APIs and that its implementation didn’t fall under fair use.
“In reviewing that decision, we assume, for argument’s sake, that the material was copyrightable. But we hold that the copying here at issue nonetheless constituted a fair use. Hence, Google’s copying did not violate the copyright law,” Justice Stephen Breyer wrote in the decision, which reverses Oracle’s previous win. Justices Samuel Alito and Clarence Thomas dissented.
“Google’s copying of the Java SE API, which included only those lines of code that were needed to allow programmers to put their accrued talents to work in a new and transformative program, was a fair use of that material as a matter of law,” Breyer wrote.
Google SVP of Global Affairs Kent Walker called the ruling, embedded below, a “big win for innovation, interoperability & computing.”
Among other technology trends accelerated by the Covid-19 pandemic, the use of contactless mobile payments boomed in 2020. According to a recent report by analyst firm eMarketer, in-store mobile payments usage grew 29% last year in the U.S., as the pandemic pushed consumers to swap out cash and credit cards for the presumably safer mobile payments option at point-of-sale.
Last year, 92.3 million U.S. consumers age 14 or older used proximity-based mobile payments at least one time during a 6-month period in 2020 — a figure the firm expects to grow to reach 101.2 million this year. And that usage is now on track to surpass half of all smartphone users by 2025, eMarketer forecasts.
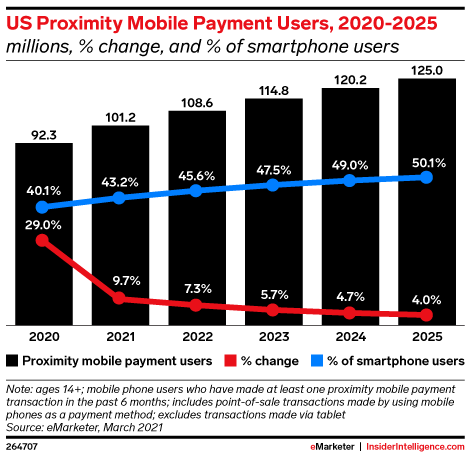
Image Credits: eMarketer
Adoption last year was largest among younger consumers, including Gen Z and millennials. The former is expected to account for more than 4 million of the total 6.5 million new mobile wallet users per year from 2021 to 2025. Millennials, meanwhile, will continue to account for around 4 in 10 mobile wallet users.
Several industry reports had already noted the pandemic impacts on the mobile wallet industry in general, with one from earlier this month by finance and investment company Finaria estimating that the industry would grow 24% from last year to reach $2.4 trillion in 2021. It had said that while Asian markets and particularly China had been leading the way in mobile payments adoption, the U.S. had earlier struggled due to the slow rollout of mobile payment technologies by retail stores. But now, the U.S. has grown to become the second-largest market with $465.1 billion worth of mobile payment transactions, which will grow to $698 billion in 2023.
The pandemic had pushed lagging retailers to finally get on board with mobile payments. A mid-year survey published in 2020 by the National Retail Federation and Forrester, found that no-touch payments had increased for 69% of retailers, and that 67% now accept some form of contactless payment, including both mobile payments and contactless cards.
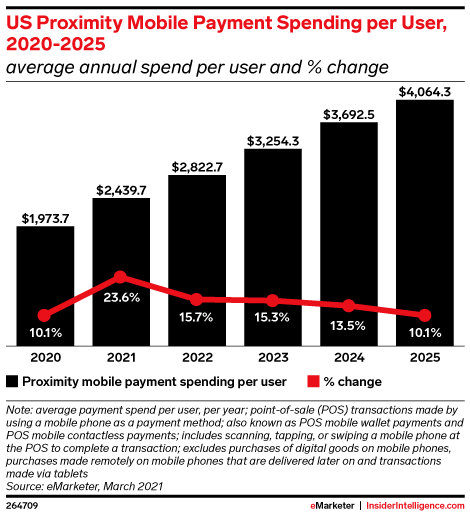
Image Credits: eMarketer
As a result of the industry changes, eMarketer reports that not only has mobile wallet usage increased, the average annual spend per user is increasing, as well. The firm predicts that figure will grow 23.6% from ~$1,973.70 in 2020 to $2,439.68 in 2021, and will surpass $3,000 by 2023.
In the U.S., Apple Pay remains the top mobile payment player with 43.9 million users in 2021, growing by 14.4 million between 2020 and 2025 — more than its competitors. Starbucks will remain the No. 2 player with 31.2 million users, followed by Google Pay, which will add 10.2 million users during that time frame. Samsung Pay, meanwhile, is seeing stagnant growth, adding just 2 million more users between 2020 and 2025.
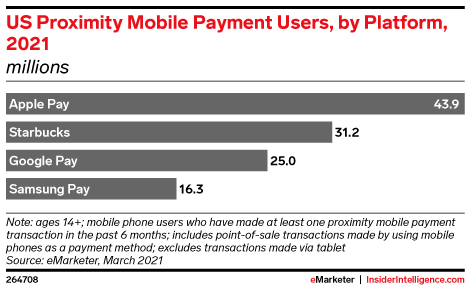
Image Credits: eMarketer
Earlier this year, we covered the demise of flexible workspace operator Knotel.
The once high-flying startup had just announced it had filed for bankruptcy and that its assets were being acquired by investor and commercial real estate brokerage Newmark for a reported $70 million.
It was a hard fall for a company that just one year prior had been valued at $1.6 billion.
It was hard to pinpoint exactly the beginning of the end for Knotel, which had raised about $560 million in funding. Some said the pandemic was the nail in Knotel’s coffin, while others pointed out the proptech was already in trouble before the pandemic hit, facing a number of lawsuits and evictions.
Then this past weekend, Knotel co-founder Amol Sarva shed some more light on the situation — essentially publicly trashing Newmark, which had co-led the startup’s $70 million Series B in 2018.
In a letter that he emailed to an unspecified group of people, Sarva points out that the company had reached “nearly $400mm of run rate in early 2020, posted gross profit, and even kept more than 2/3 of revenue intact while doing everything we could to support customer continuity and work with landlord partners amicably.”
He went on to describe Newmark as “a stalking horse” that used bankruptcy to take control of Knotel with around $100 million of new capital. That process, he said, undermined important relationships and “hurt lots of customers and partners.”
“I’m so disappointed that this was the direction pressed. The process made clear to me that I would not choose to be part of the new owners’ way of moving forward,” Sarva continued.
He further criticized Newmark, saying the brokerage has hired “a group of Adam Neuman-era (sic) WeWork bros to lead the company forward.”
Newmark had not yet responded to a request for comment at the time of writing. While it’s safe to say that Sarva is bitter about the way things turned out, it would be interesting to know exactly at what point he came to this conclusion.
He did say that he’s heading back to the lab where Knotel was invented originally, as co-founder/CEO of Knote.
Spotify is opening up its personalized playlist, “On Repeat,” to advertising sponsorship. This playlist, launched in 2019 and featuring users’ favorite songs, is only the second personalized playlist on the music streaming service that’s being made available for sponsorship. Spotify’s flagship playlist, “Discover Weekly,” became the first in 2019.
The sponsorship is made possible through the company’s Sponsored Playlist ad product, which gives brands the ability to market to Spotify’s free users with audio, video and display ad messages across breaks, allowing the advertiser to own the experience “end-to-end,” the company says.
It also gives brands an opportunity to reach Spotify’s most engaged users.
When Spotify opened up “Discover Weekly” to sponsorship, for example, it noted that users who listened to this playlist streamed more than double those who didn’t. Similarly, “On Repeat” caters to Spotify’s more frequent users because of its focus on tracks users have played most often.
Since the launch of “On Repeat” in September 2019, Spotify says the playlist has reached 12 billion streams globally. Fans have also spent over 750 million hours listening to the playlist, where artists like Bad Bunny, The Weeknd, and Ariana Grande have topped the list for “most repeated” listens.
Though Spotify today offers its numerous owned and operated playlists for sponsorship, its personalized playlists have largely been off-limits — except for “Discover Weekly.” These are highly-valued properties, as Spotify directs users to stream collections powered by its algorithms, which Spotify organizes in its ever-expanding “Made for You” hub in its app. Here, users can jump in between “Discover Weekly,” and other collections organized by genre, artist, decade, and more — like new releases, favorites, suggestions, and more.
With the launch of sponsorship for “On Repeat,” brands across 30 global markets, including North America, Europe, Latin America and Asia-Pacific will be able to own another of Spotify’s largest personalized properties for a time.
The first U.S. advertiser to take advantage of the sponsorship is TurboTax, which cited the personalization elements and user engagement with the playlist among the reasons why the ad product made sense for them.
“Like music, taxes are not one size fits all. Every tax situation is unique and every individual’s needs are different,” said Cathleen Ryan, VP of Marketing for TurboTax, in a statement about the launch. “We’re using Spotify’s deep connection to its engaged listeners to get in front of consumers and show them that with TurboTax you can get the expertise you need on your terms. With Spotify, we’re able to get both reach and unique targeting that ensures the right audiences know about the tools, guidance and expertise that TurboTax offers,” she added.
Over the course of their careers, Alex Bovee and Paul Querna realized that while the use of SaaS apps and cloud infrastructure was exploding, the process to give employees permission to use them was not keeping up.
The pair led Zero Trust strategies and products at Okta, and could see the problem firsthand. For the unacquainted, Zero Trust is a security concept based on the premise that organizations should not automatically trust anything inside or outside its perimeters and, instead must verify anything and everything trying to connect to its systems before granting access.
Bovee and Querna realized that while more organizations were adopting Zero Trust strategies, they were not enacting privilege controls. This was resulting in delayed employee access to apps, or to the over-permissioning employees from day one.
Last summer, Bovee left Okta to be the first virtual entrepreneur-in-residence at VC firm Accel. There, he and Accel partner Ping Li got to talking and realized they both had an interest in addressing the challenge of granting permissions to users of cloud apps quicker and more securely.
Recalls Li: “It was actually kind of fortuitous. We were looking at this problem and I was like ‘Who can we talk to about the space? And we realized we had an expert in Alex.”
At that point, Bovee told Li he was actually thinking of starting a company to solve the problem. And so he did. Months later, Querna left Okta to join him in getting the startup off the ground. And today, ConductorOne announced that it raised $5 million in seed funding in a round led by Accel, with participation from Fuel Capital, Fathom Capital and Active Capital.
ConductorOne plans to use its new capital to build what the company describes as “the first-ever identity orchestration and automation platform.” Its goal is to give IT and identity admins the ability to automate and delegate employee access to cloud apps and infrastructure, while preserving least privilege permissions.
“The crux of the problem is that you’ve got these identities — you’ve got employees and contractors on one side and then on the other side you’ve got all this SaaS infrastructure and they all have sort of infinite permutations of roles and permissions and what people can do within the context of those infrastructure environments,” Bovee said.
Companies of all sizes often have hundreds of apps and infrastructure providers they’re managing. It’s not unusual for an IT helpdesk queue to be more than 20% access requests, with people needing urgent access to resources like Salesforce, AWS, or GitHub, according to Bovee. Yet each request is manually reviewed to make sure people get the right level of permissions.
“But that access is never revoked, even if it’s unused,” Bovee said. “Without a central layer to orchestrate and automate authorization, it’s impossible to handle all the permissions, entitlements, and on- and off-boarding, not to mention auditing and analytics.”
ConductorOne aims to build “the world’s best access request experience,” with automation at its core.
“Automation that solves privilege management and governance is the next major pillar of cloud identity,” Accel’s Li said.
Bovee and Querna have deep expertise in the space. Prior to Okta, Bovee led enterprise mobile security product development at Lookout. Querna was the co-founder and CTO of ScaleFT, which was acquired by Okta in 2018. He also led technology and strategy teams at Rackspace and Cloudkick, and is a vocal and active open source software advocate.
While the company’s headquarters are in Portland, Oregon, ConductorOne is a remote-first company with 10 employees.
“We’re deep in building the product right now, and just doing a lot of customer development to understand the problems deeply,” Bovee said. “Then we’ll focus on getting early customers.”